Phase 1/2 Randomized Study of the Immunogenicity, Safety, and Tolerability of a Respiratory Syncytial Virus Prefusion F Vaccine in Adults With Concomitant Inactivated Influenza Vaccine
- PMID: 34931667
- PMCID: PMC9200152
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiab611
Phase 1/2 Randomized Study of the Immunogenicity, Safety, and Tolerability of a Respiratory Syncytial Virus Prefusion F Vaccine in Adults With Concomitant Inactivated Influenza Vaccine
Abstract
Background: Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) causes substantial morbidity and mortality in older adults and adults with comorbidities. An effective vaccine is needed. An investigational bivalent prefusion F vaccine (RSVpreF) was assessed in healthy adults.
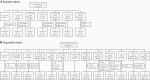
Methods: This phase 1/2 study randomized adults 18-85 years old to receive placebo or 60, 120, or 240 µg RSVpreF (with or without aluminum hydroxide) alone or concomitantly with seasonal inactivated influenza vaccine (SIIV). Safety and immunogenicity were assessed.
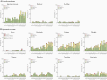
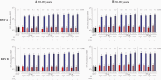
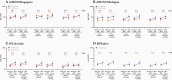
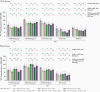
Results: In older adults, reactogenicity events were predominantly mild or moderate among RSVpreF recipients; adverse events through 1 month postvaccination were similar across formulations. Coadministration with SIIV did not appear to affect safety among younger or older adults. All RSVpreF formulations with or without concomitant SIIV elicited robust RSV serum-neutralizing responses in adults aged 50-85 years 1 month postvaccination. Neutralizing titers 1 and 12 months postvaccination were 6.9-14.9 and 2.9-4.5 times, respectively, those before vaccination. SIIV immune responses trended lower when coadministered with RSVpreF.
Conclusions: RSVpreF formulations administered alone or with SIIV were well tolerated and highly immunogenic in older adults, supporting the potential for RSVpreF to protect older adults from RSV disease.
Clinical trials registration: NCT03529773.
Keywords: F protein; immunogenicity; older adults; respiratory syncytial virus; safety; vaccine.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures

Comment in
-
Are We Ready for Maternal Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccination?J Infect Dis. 2022 Jun 15;225(12):2053-2055. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiab613. J Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 34932123 No abstract available.
References
-
- Li Y, Johnson EK, Shi T, et al. . National burden estimates of hospitalisations for acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in young children in 2019 among 58 countries: a modelling study. Lancet Respir Med 2021; 9:175–85. - PubMed
-
- Falsey AR, Hennessey PA, Formica MA, Cox C, Walsh EE.. Respiratory syncytial virus infection in elderly and high-risk adults. N Engl J Med 2005; 352:1749–59. - PubMed

