MicroRNA miR-4709-3p targets Large Tumor Suppressor Kinase 2 (LATS2) and induces obstructive renal fibrosis through Hippo signaling
- PMID: 34931960
- PMCID: PMC8810092
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2002493
MicroRNA miR-4709-3p targets Large Tumor Suppressor Kinase 2 (LATS2) and induces obstructive renal fibrosis through Hippo signaling
Abstract
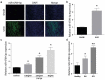
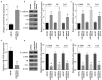
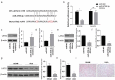
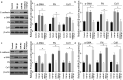
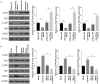
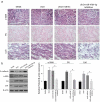
Obstructive renal fibrosis is the consequence of abnormal extracellular matrix assembly, which eventually results in renal failure, acute, and end‑stage renal infection. MicroRNAs (miRNAs), a particular category of small RNAs, modulate the expression of genes post-transcriptionally and regulate biological activities, including fibrogenesis. The study probed to estimate the key functions of miR-4709-3p in obstructive renal fibrosis. This investigation used TGF-β1 stimulated HK-2 in-vitro model, unilateral ureteral occlusion (UUO) mice model, and human Diabetic nephropathy (DN) and Renal interstitial fibrosis (RIF) specimens to depict the abundance of the miR-4709-3p level using FISH and RT-qPCR. MiR-4709-3p mimics and inhibitors were utilized to evaluate the functions of miR-4709-3p in-vitro. Luciferase assay was exploited to verify miR-4709-3p and LATS2 3'UTR binding. Finally, to depict the functions of miR-4709-3p in-vivo, the UUO model was injected with miR-4709-3p inhibitors. Results exhibited the upregulation of miR-4709-3p in UUO-induced in-vivo model, TGF-β1 stimulated HK-2, and human RIF and DN samples. Moreover, it was determined that modulating miR-4709-3p regulated the level of fibrosis markers. Luciferase assay miR-4709-3p modulates renal fibrosis by targeting LATS2. Finally, it was found that miR-4709-3p regulates obstructive renal fibrosis through the Hippo signaling pathway. Overall, the study concludes that aberrant miR-4709-3p expression plays an essential function in the renal fibrosis progression, and miR-4709-3p overexpression could advance obstructive renal fibrosis via LATS2 targeting in Hippo signaling pathway. Therefore, miR-4709-3p inhibition may be a potential renal fibrosis therapy target.
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease (CKD); Hippo signaling; miR-4709-3p; unilateral ureteric obstruction (UUO).
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
miR-130a-3p inhibition protects against renal fibrosis in vitro via the TGF-β1/Smad pathway by targeting SnoN.Exp Mol Pathol. 2020 Feb;112:104358. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2019.104358. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Exp Mol Pathol. 2020. PMID: 31836508
-
Mechanistic study on lncRNA XIST/miR-124-3p/ITGB1 axis in renal fibrosis in obstructive nephropathy.Exp Cell Res. 2024 Sep 1;442(1):114194. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2024.114194. Epub 2024 Aug 9. Exp Cell Res. 2024. PMID: 39127440
-
MiR-27b-3p inhibits the progression of renal fibrosis via suppressing STAT1.Hum Cell. 2021 Mar;34(2):383-393. doi: 10.1007/s13577-020-00474-z. Epub 2021 Jan 17. Hum Cell. 2021. PMID: 33454903 Free PMC article.
-
The critical role of the Hippo signaling pathway in renal fibrosis.Cell Signal. 2025 Jun;130:111661. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2025.111661. Epub 2025 Feb 21. Cell Signal. 2025. PMID: 39988289 Review.
-
Research progress on miR-124-3p in the field of kidney disease.BMC Nephrol. 2024 Aug 7;25(1):252. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03688-7. BMC Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 39112935 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MiR-449a downregulation alleviates the progression of renal interstitial fibrosis by mediating the KLF4/MFN2 axis.Int Urol Nephrol. 2023 Jul;55(7):1837-1846. doi: 10.1007/s11255-023-03503-6. Epub 2023 Feb 12. Int Urol Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 36781680
-
Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells improve the survial of flaps by promoting angiogenesis in mice.Eur J Med Res. 2025 May 2;30(1):356. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02602-7. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40312717 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomics reveals the key transcription-related factors mediating obstructive nephropathy in pediatric patients and mice.Ren Fail. 2025 Dec;47(1):2443032. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2443032. Epub 2025 Jan 1. Ren Fail. 2025. PMID: 39743726 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting CC chemokine ligand (CCL) 20 by miR-143-5p alleviate lead poisoning-induced renal fibrosis by regulating interstitial fibroblasts excessive proliferation and dysfunction.Bioengineered. 2022 Apr;13(4):11156-11168. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2062106. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35485286 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Humphreys BDJAROP. Mechanisms of renal fibrosis. Annual review of physiology. 2018;80:309–326. - PubMed
-
- Kawanami D, Matoba K, Utsunomiya K. Signaling pathways in diabetic nephropathy. Histol Histopathol. 2016;31(10):1059–1067. - PubMed
-
- Zhou Y, Lv C, Wu C, et al. Suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) 2 attenuates renal lesions in rats with diabetic nephropathy. Acta Histochem. 2014;116(5):981–988. - PubMed
-
- Sun YBY, Qu X, Caruana G, et al. The origin of renal fibroblasts/myofibroblasts and the signals that trigger fibrosis. ResearchGate. 2016;92(3):102–107. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
