MicroRNA miR-4709-3p targets Large Tumor Suppressor Kinase 2 (LATS2) and induces obstructive renal fibrosis through Hippo signaling
- PMID: 34931960
- PMCID: PMC8810092
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2002493
MicroRNA miR-4709-3p targets Large Tumor Suppressor Kinase 2 (LATS2) and induces obstructive renal fibrosis through Hippo signaling
Abstract
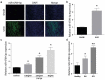
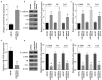
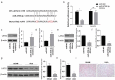
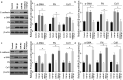
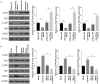
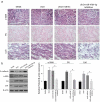
Obstructive renal fibrosis is the consequence of abnormal extracellular matrix assembly, which eventually results in renal failure, acute, and end‑stage renal infection. MicroRNAs (miRNAs), a particular category of small RNAs, modulate the expression of genes post-transcriptionally and regulate biological activities, including fibrogenesis. The study probed to estimate the key functions of miR-4709-3p in obstructive renal fibrosis. This investigation used TGF-β1 stimulated HK-2 in-vitro model, unilateral ureteral occlusion (UUO) mice model, and human Diabetic nephropathy (DN) and Renal interstitial fibrosis (RIF) specimens to depict the abundance of the miR-4709-3p level using FISH and RT-qPCR. MiR-4709-3p mimics and inhibitors were utilized to evaluate the functions of miR-4709-3p in-vitro. Luciferase assay was exploited to verify miR-4709-3p and LATS2 3'UTR binding. Finally, to depict the functions of miR-4709-3p in-vivo, the UUO model was injected with miR-4709-3p inhibitors. Results exhibited the upregulation of miR-4709-3p in UUO-induced in-vivo model, TGF-β1 stimulated HK-2, and human RIF and DN samples. Moreover, it was determined that modulating miR-4709-3p regulated the level of fibrosis markers. Luciferase assay miR-4709-3p modulates renal fibrosis by targeting LATS2. Finally, it was found that miR-4709-3p regulates obstructive renal fibrosis through the Hippo signaling pathway. Overall, the study concludes that aberrant miR-4709-3p expression plays an essential function in the renal fibrosis progression, and miR-4709-3p overexpression could advance obstructive renal fibrosis via LATS2 targeting in Hippo signaling pathway. Therefore, miR-4709-3p inhibition may be a potential renal fibrosis therapy target.
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease (CKD); Hippo signaling; miR-4709-3p; unilateral ureteric obstruction (UUO).
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Humphreys BDJAROP. Mechanisms of renal fibrosis. Annual review of physiology. 2018;80:309–326. - PubMed
-
- Kawanami D, Matoba K, Utsunomiya K. Signaling pathways in diabetic nephropathy. Histol Histopathol. 2016;31(10):1059–1067. - PubMed
-
- Zhou Y, Lv C, Wu C, et al. Suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) 2 attenuates renal lesions in rats with diabetic nephropathy. Acta Histochem. 2014;116(5):981–988. - PubMed
-
- Sun YBY, Qu X, Caruana G, et al. The origin of renal fibroblasts/myofibroblasts and the signals that trigger fibrosis. ResearchGate. 2016;92(3):102–107. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
