Whole-transcriptome analysis in acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a report from the DFCI ALL Consortium Protocol 16-001
- PMID: 34933343
- PMCID: PMC8864659
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2021005634
Whole-transcriptome analysis in acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a report from the DFCI ALL Consortium Protocol 16-001
Abstract
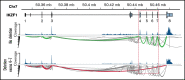
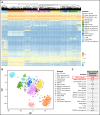
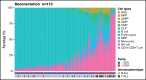
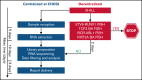
The molecular hallmark of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is characterized by recurrent, prognostic genetic alterations, many of which are cryptic by conventional cytogenetics. RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) is a powerful next-generation sequencing technology that can simultaneously identify cryptic gene rearrangements, sequence mutations and gene expression profiles in a single assay. We examined the feasibility and utility of incorporating RNA-seq into a prospective multicenter phase 3 clinical trial for children with newly diagnosed ALL. The Dana-Farber Cancer Institute ALL Consortium Protocol 16-001 enrolled 173 patients with ALL who consented to optional studies and had samples available for RNA-seq. RNA-seq identified at least 1 alteration in 157 patients (91%). Fusion detection was 100% concordant with results obtained from conventional cytogenetic analyses. An additional 56 gene fusions were identified by RNA-seq, many of which confer prognostic or therapeutic significance. Gene expression profiling enabled further molecular classification into the following B-cell ALL (B-ALL) subgroups: high hyperdiploid (n = 36), ETV6-RUNX1/-like (n = 31), TCF3-PBX1 (n = 7), KMT2A-rearranged (KMT2A-R; n = 5), intrachromosomal amplification of chromosome 21 (iAMP21) (n = 1), hypodiploid (n = 1), Philadelphia chromosome (Ph)-positive/Ph-like (n = 16), DUX4-R (n = 11), PAX5 alterations (PAX5 alt; n = 11), PAX5 P80R (n = 1), ZNF384-R (n = 4), NUTM1-R (n = 1), MEF2D-R (n = 1), and others (n = 10). RNA-seq identified 141 nonsynonymous mutations in 93 patients (54%); the most frequent were RAS-MAPK pathway mutations. Among 79 patients with both low-density array and RNA-seq data for the Philadelphia chromosome-like gene signature prediction, results were concordant in 74 patients (94%). In conclusion, RNA-seq identified several clinically relevant genetic alterations not detected by conventional methods, which supports the integration of this technology into front-line pediatric ALL trials. This trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT03020030.
© 2022 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, et al., eds. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2010. National Cancer Institute Bethesda, MD, based on November 2012 SEER data submission, posted to the SEER web site, April 2013. https://seer.cancer.gov/archive/csr/1975_2010/
-
- Hunger SP, Mullighan CG. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(16):1541-1552. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

