Ethics and society review: Ethics reflection as a precondition to research funding
- PMID: 34934006
- PMCID: PMC8719852
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2117261118
Ethics and society review: Ethics reflection as a precondition to research funding
Abstract
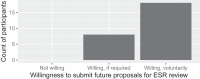
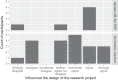
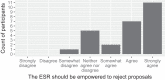
Researchers in areas as diverse as computer science and political science must increasingly navigate the possible risks of their research to society. However, the history of medical experiments on vulnerable individuals influenced many research ethics reviews to focus exclusively on risks to human subjects rather than risks to human society. We describe an Ethics and Society Review board (ESR), which fills this moral gap by facilitating ethical and societal reflection as a requirement to access grant funding: Researchers cannot receive grant funding from participating programs until the researchers complete the ESR process for their proposal. Researchers author an initial statement describing their proposed research's risks to society, subgroups within society, and globally and commit to mitigation strategies for these risks. An interdisciplinary faculty panel iterates with the researchers to refine these risks and mitigation strategies. We describe a mixed-method evaluation of the ESR over 1 y, in partnership with a large artificial intelligence grant program at our university. Surveys and interviews of researchers who interacted with the ESR found 100% (95% CI: 87 to 100%) were willing to continue submitting future projects to the ESR, and 58% (95% CI: 37 to 77%) felt that it had influenced the design of their research project. The ESR panel most commonly identified issues of harms to minority groups, inclusion of diverse stakeholders in the research plan, dual use, and representation in datasets. These principles, paired with possible mitigation strategies, offer scaffolding for future research designs.
Keywords: computer science; ethics; machine learning; societal consequences.
Copyright © 2021 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

References
-
- Benjamin R., Race After Technology: Abolitionist Tools for the New Jim Code (John Wiley & Sons, 2019).
-
- Rittel H. W., Webber M. M., Dilemmas in a general theory of planning. Policy Sci. 4, 155–169 (1973).
-
- Department of Health, Education, and Welfare, “The Belmont Report: Ethical principles and guidelines for the protection of human subjects of research” (Department of Health, Education, and Welfare, 1979). - PubMed
-
- United States Department of Health and Human Services, Common rule. Code Fed. Regul. Title 45, §46.111 (2018).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

