Rosin Soap Exhibits Virucidal Activity
- PMID: 34935417
- PMCID: PMC8693916
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.01091-21
Rosin Soap Exhibits Virucidal Activity
Abstract
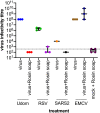
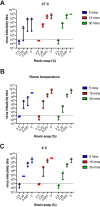
Chemical methods of virus inactivation are used routinely to prevent viral transmission in both a personal hygiene capacity but also in at-risk environments like hospitals. Several virucidal products exist, including hand soaps, gels, and surface disinfectants. Resin acids, which can be derived from tall oil, produced from trees, have been shown to exhibit antibacterial activity. However, whether these products or their derivatives have virucidal activity is unknown. Here, we assessed the capacity of rosin soap to inactivate a panel of pathogenic mammalian viruses in vitro. We show that rosin soap can inactivate human enveloped viruses: influenza A virus (IAV), respiratory syncytial virus, and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). For IAV, rosin soap could provide a 100,000-fold reduction in infectivity. However, rosin soap failed to affect the nonenveloped encephalomyocarditis virus (EMCV). The inhibitory effect of rosin soap against IAV infectivity was dependent on its concentration but not on the incubation time or temperature. In all, we demonstrate a novel chemical inactivation method against enveloped viruses, which could be of use for preventing virus infections in certain settings. IMPORTANCE Viruses remain a significant cause of human disease and death, most notably illustrated through the current coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. Control of virus infection continues to pose a significant global health challenge to the human population. Viruses can spread through multiple routes, including via environmental and surface contamination, where viruses can remain infectious for days. Methods for inactivating viruses on such surfaces may help mitigate infection. Here, we present evidence identifying a novel virucidal product, rosin soap, which is produced from tall oil from coniferous trees. Rosin soap was able to rapidly and potently inactivate influenza virus and other enveloped viruses.
Keywords: antimicrobial; antiviral; fomite; inactivation; soap; virucidal; virus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare a conflict of interest. This work was supported through funding from the associated commercial companies (Hankkija Oy, and Forchem Oy). The funders/company (HK, JV and JO) played no part in the design or interpretation of results. Some of the authors (SB, DF, CGGB and JM) have a patent pending on the use of rosin soap as a virucidal agent, and consult on the use of such agents as antimicrobial products with Hankkija Oy, and Forchem Oy.
Figures

References
-
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation. 2019. Global burden of disease study 2019 (GBD 2019) data resources. GHDx. http://ghdx.healthdata.org/gbd-2019.
-
- Iuliano AD, Roguski KM, Chang HH, Muscatello DJ, Palekar R, Tempia S, Cohen C, Gran JM, Schanzer D, Cowling BJ, Wu P, Kyncl J, Ang LW, Park M, Redlberger-Fritz M, Yu H, Espenhain L, Krishnan A, Emukule G, van Asten L, Pereira da Silva S, Aungkulanon S, Buchholz U, Widdowson M-A, Bresee JS, Azziz-Baumgartner E, Cheng P-Y, Dawood F, Foppa I, Olsen S, Haber M, Jeffers C, MacIntyre CR, Newall AT, Wood JG, Kundi M, Popow-Kraupp T, Ahmed M, Rahman M, Marinho F, Sotomayor Proschle CV, Vergara Mallegas N, Luzhao F, Sa L, Barbosa-Ramírez J, Sanchez DM, Gomez LA, Vargas XB, Acosta Herrera a, Llanés MJ, et al. . 2018. Estimates of global seasonal influenza-associated respiratory mortality: a modelling study. Lancet 391:1285–1300. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(17)33293-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. 2021. WHO COVID-19 Dashboard. https://covid19.who.int.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

