Registry for Acute Coronary Events in Nigeria (RACE-Nigeria): Clinical Characterization, Management, and Outcome
- PMID: 34935419
- PMCID: PMC9075212
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.120.020244
Registry for Acute Coronary Events in Nigeria (RACE-Nigeria): Clinical Characterization, Management, and Outcome
Abstract
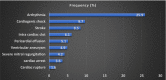
Background Coronary artery disease was hitherto a rarity in Africa. Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) accounts for coronary artery disease-related morbidity and mortality. Reports on ACS in Africa are few. Methods and Results We enrolled 1072 indigenous Nigerian people 59.2±12.4 years old (men, 66.8%) with ACS in an observational multicentered national registry (2013-2018). Outcome measures included incidence, intervention times, reperfusion rates, and 1-year mortality. The incidence of ACS was 59.1 people per 100 000 hospitalized adults per year, and comprised ST-segment-elevation myocardial infarction (48.7%), non-ST-segment-elevation myocardial infarction (24.5%), and unstable angina (26.8%). ACS frequency peaked 10 years earlier in men than women. Patients were predominantly from urban settings (87.3%). Median time from onset of symptoms to first medical contact (patients with ST-segment-elevation myocardial infarction) was 6 hours (interquartile range, 20.1 hours), and only 11.9% presented within a 12-hour time window. Traditional risk factors of coronary artery disease were observed. The coronary angiography rate was 42.4%. Reperfusion therapies included thrombolysis (17.1%), percutaneous coronary intervention (28.6%), and coronary artery bypass graft (11.2%). Guideline-based pharmacotherapy was adequate. Major adverse cardiac events were 30.8%, and in-hospital mortality was 8.1%. Mortality rates at 30 days, 3 months, 6 months, and 1 year were 8.7%, 9.9%, 10.9%, and 13.3%, respectively. Predictors of mortality included resuscitated cardiac arrest (odds ratio [OR], 50.0; 95% CI, 0.010-0.081), nonreperfusion (OR, 34.5; 95% CI, 0.004-0.221), pulmonary edema (OR, 11.1; 95% CI, 0.020-0.363), left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (OR, 4.1; 95% CI, 0.091-0.570), and left ventricular systolic dysfunction (OR, 2.1; 95% CI, 1.302-3.367). Conclusions ACS burden is rising in Nigeria, and patients are relatively young and from an urban setting. The system of care is evolving and is characterized by lack of capacity and low patient eligibility for reperfusion. We recommend preventive strategies and health care infrastructure-appropriate management guidelines.
Keywords: acute coronary syndrome; incidence; intervention times; reperfusion mortality.
Figures


References
-
- Becker BJP. Cardio‐vascular disease in the Bantu and coloured races of South Africa. IV. Atheromatosis. S Afr Med J. 1946;11:97–105. - PubMed
-
- Davis JNP. Pathology of Central African natives. Mulago hospital postmortem studies IX. Cardiovascular disease. East Afr Med J. 1948;25:459–461. - PubMed
-
- Seftel HC, Kew MC. Myocardial infarction in the Johannesburg Bantu. S Afr Med J. 1970;44:8–12. - PubMed
-
- Falase AO, Cole TO, Osuntukun BO. Myocardial infarction in Nigeria. Trop Geogr Med. 1973;25:147–150. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

