Stepwise disassembly of GABAergic synapses during pathogenic excitotoxicity
- PMID: 34936876
- PMCID: PMC8824488
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.110142
Stepwise disassembly of GABAergic synapses during pathogenic excitotoxicity
Abstract
GABAergic synaptic inhibition controls neuronal firing, excitability, and synaptic plasticity to regulate neuronal circuits. Following an acute excitotoxic insult, inhibitory synapses are eliminated, reducing synaptic inhibition, elevating circuit excitability, and contributing to the pathophysiology of brain injuries. However, mechanisms that drive inhibitory synapse disassembly and elimination are undefined. We find that inhibitory synapses are disassembled in a sequential manner following excitotoxicity: GABAARs undergo rapid nanoscale rearrangement and are dispersed from the synapse along with presynaptic active zone components, followed by the gradual removal of the gephyrin scaffold, prior to complete elimination of the presynaptic terminal. GABAAR nanoscale reorganization and synaptic declustering depends on calcineurin signaling, whereas disassembly of gephyrin relies on calpain activation, and blockade of both enzymes preserves inhibitory synapses after excitotoxic insult. Thus, inhibitory synapse disassembly occurs rapidly, with nanoscale precision, in a stepwise manner and most likely represents a critical step in the progression of hyperexcitability following excitotoxicity.
Keywords: GABA(A) receptor; OGD; SIM; calcineurin; calpain; dSTORM; gephyrin; inhibitory synapse; ischemia; super-resolution microscopy.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
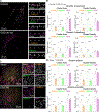

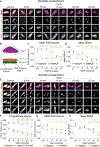
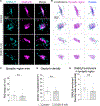
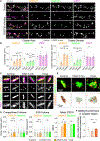


References
-
- Alicke B, and Schwartz-Bloom RD (1995). Rapid down-regulation of GABAA receptors in the gerbil hippocampus following transient cerebral ischemia. J. Neurochem 65, 2808–2811. - PubMed
-
- Almeida-Suhett CP, Prager EM, Pidoplichko V, Figueiredo TH, Marini AM, Li Z, Eiden LE, and Braga MF (2015). GABAergic interneuronal loss and reduced inhibitory synaptic transmission in the hippocampal CA1 region after mild traumatic brain injury. Exp. Neurol 273, 11–23. - PubMed
-
- Bannai H, Lévi S, Schweizer C, Inoue T, Launey T, Racine V, Sibarita J-B, Mikoshiba K, and Triller A. (2009). Activity-dependent tuning of inhibitory neurotransmission based on GABAAR diffusion dynamics. Neuron 62, 670–682. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 MH119154/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R35 NS116879/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS092645/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007635/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS040701/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 MH123053/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH123700/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 19PRE34380542/AHA/American Heart Association-American Stroke Association/United States
- F99 NS120640/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS048154/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS046072/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K00 MH134674/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK116073/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

