Enhancing efficacy of existing antibacterials against selected multiple drug resistant bacteria using cinnamic acid-coated magnetic iron oxide and mesoporous silica nanoparticles
- PMID: 34937524
- PMCID: PMC9518276
- DOI: 10.1080/20477724.2021.2014235
Enhancing efficacy of existing antibacterials against selected multiple drug resistant bacteria using cinnamic acid-coated magnetic iron oxide and mesoporous silica nanoparticles
Abstract
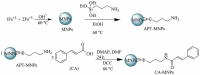
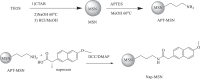
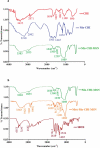
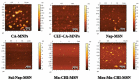
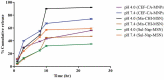
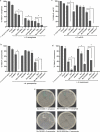
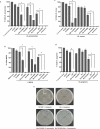
Developing new antibacterial drugs by using traditional ways is insufficient to meet existing challenges; hence, new strategies in the field of antibacterial discovery are necessary. An alternative strategy is to improve the efficacy of currently available antibiotics. Herein, the antibacterial efficacy of drugs (Cefixime, Sulfamethoxazole, and Moxifloxacin) and drug-loaded cinnamic acid-coated magnetic iron oxide and mesoporous silica nanoparticles (NPs) was elucidated versus Gram-negative bacteria (Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella pneumoniae, neuropathogenic Escherichia coli K1 and Serratia marcescens) and Gram-positive bacteria (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Bacillus cereus). NPs were synthesized by co-precipitation and the Stöber method, and characterized by Fourier transform-infrared spectroscopy, Zetasizer, and Atomic force microscopy. Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) assays were accomplished to determine drug cytotoxicity against human cells. Spherical NPs in the range of 118-362 nm were successfully synthesized. Antibacterial assays revealed that drugs conjugated with NPs portray enhanced bactericidal efficacies against multiple drug resistant bacteria compared to the drugs alone. Of note, Cefixime-conjugated NPs against Escherichia coli K1 and Methicillin- resistant Staphylococcus aureus, resulted in the complete eradication of all bacterial isolates tested at significantly lower concentrations compared to the antibiotics alone. Likewise, conjugation of Moxifloxacin resulted in the complete elimination of E. coli K1 and MRSA. Of note, nano-formulated drugs presented negligible cytotoxicity against human cells. These results depict potent, and enhanced efficacy of nano-formulated drugs against medically important bacteria and can be used as alternatives to current antibiotics. Future in vivo studies and clinical studies are warranted in prospective years to realize these expectations.
Keywords: Antibiotic resistance; MBC; cytotoxicity; drug discovery; infectious diseases; magnetic nanoparticles; mic; multi-drug resistance; nanotechnology.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures




Similar articles
-
Hesperidin-, Curcumin-, and Amphotericin B- Based Nano-Formulations as Potential Antibacterials.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 May 20;11(5):696. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11050696. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35625340 Free PMC article.
-
Moxifloxacin and Sulfamethoxazole-Based Nanocarriers Exhibit Potent Antibacterial Activities.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Aug 11;10(8):964. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10080964. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34439014 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc oxide nanoparticles conjugated with clinically-approved medicines as potential antibacterial molecules.AMB Express. 2021 Jul 10;11(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s13568-021-01261-1. AMB Express. 2021. PMID: 34245385 Free PMC article.
-
Literature review on the distribution characteristics and antimicrobial resistance of bacterial pathogens in neonatal sepsis.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2022 Mar;35(5):861-870. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2020.1732342. Epub 2020 Feb 26. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2022. PMID: 32102584 Review.
-
Nano delivery systems to the rescue of ciprofloxacin against resistant bacteria "E. coli; P. aeruginosa; Saureus; and MRSA" and their infections.J Control Release. 2022 Sep;349:338-353. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.07.003. Epub 2022 Jul 12. J Control Release. 2022. PMID: 35820538 Review.
Cited by
-
Antibacterial Properties of Ethacridine Lactate and Sulfmethoxazole Loaded Functionalized Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Apr 14;12(4):755. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12040755. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37107117 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Nanostructures for Antimicrobial Therapy.Materials (Basel). 2022 Mar 24;15(7):2388. doi: 10.3390/ma15072388. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35407720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibacterial effects of quercetagetin are significantly enhanced upon conjugation with chitosan engineered copper oxide nanoparticles.Biometals. 2024 Feb;37(1):171-184. doi: 10.1007/s10534-023-00539-0. Epub 2023 Oct 4. Biometals. 2024. PMID: 37792257
-
Hesperidin-, Curcumin-, and Amphotericin B- Based Nano-Formulations as Potential Antibacterials.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 May 20;11(5):696. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11050696. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35625340 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Farha MA, Brown ED.. Drug repurposing for antimicrobial discovery. Nat Microbiol. 2019;4(4):565–577. - PubMed
-
- Odonkor ST, Addo KK.. Bacteria resistance to antibiotics: recent trends and challenges. Int J Biol Med Res. 2011;2(4):1204–1210.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
