Botulinum Toxin Type A for Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 34938114
- PMCID: PMC8687679
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S340390
Botulinum Toxin Type A for Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Purpose: Botulinum toxin type A (BTX-A) has been proposed as a treatment for painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN). This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to assess the effect and safety of BTX-A for treating DPN pain.
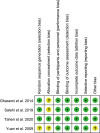
Methods: PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library were searched for relevant articles published up to July 7, 2021. Randomized clinical trials (RCTs) were included if they were related to the treatment of DPN pain with BTX-A. The primary outcome was the change in intensity of pain and secondary outcomes were adverse effects and changes in sleep and life quality.
Results: A total of four studies, comprising 231 patients, were included in our systematic review. BTX-A treatment induced a greater reduction in the visual analog scale score (mean difference = -2.52, 95% confidence interval [CI] [-3.06, -1.99], p < 0.001) than did the placebo treatment, with no significant heterogeneity between studies (I2 = 0). BTX-A treatment improved several neuropathy pain scale items (eg, hot sensation, sensitive sensation, unpleasant sensation, deep pain, and surface pain) significantly more than with placebo treatment (p < 0.05 for all). There was no significant difference in adverse effect (relative risk = 1.00, 95% CI [0.97, 1.03], p = 0.89).
Conclusion: Intradermal BTX-A injection was shown to be effective and safe in relieving DPN pain. Further larger scale and well-designed RCTs are needed.
Keywords: botulinum toxin; diabetes; peripheral neuropathic pain; systematic review.
© 2021 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures





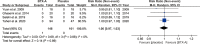
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

