Preclinical Immune Response and Safety Evaluation of the Protein Subunit Vaccine Nanocovax for COVID-19
- PMID: 34938290
- PMCID: PMC8685539
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.766112
Preclinical Immune Response and Safety Evaluation of the Protein Subunit Vaccine Nanocovax for COVID-19
Abstract
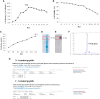
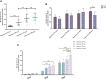
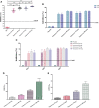
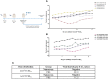
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has become a global health concern. The development of vaccines with high immunogenicity and safety is crucial for controlling the global COVID-19 pandemic and preventing further illness and fatalities. Here, we report the development of a SARS-CoV-2 vaccine candidate, Nanocovax, based on recombinant protein production of the extracellular (soluble) portion of the spike (S) protein of SARS-CoV-2. The results showed that Nanocovax induced high levels of S protein-specific IgG and neutralizing antibodies in three animal models: BALB/c mouse, Syrian hamster, and a non-human primate (Macaca leonina). In addition, a viral challenge study using the hamster model showed that Nanocovax protected the upper respiratory tract from SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nanocovax did not induce any adverse effects in mice (Mus musculus var. albino) and rats (Rattus norvegicus). These preclinical results indicate that Nanocovax is safe and effective.
Keywords: ACE2; CHO; COVID-19; RBD; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2021 Tran, May, Ung, Nguyen, Nguyen, Dinh, Doan, Tran, Khong, Nguyen, Hua, Nguyen, Ha, Phan, Nguyen, Bui, Tu, Nguyen, Le, Dong, Huynh, Ho, Le, Truong, Pham, Luong, Y, Cao, Nguyen, Le, Vuong, Nguyen and Do.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors except TTL, DCV and LKHN were employed by Nanogen Pharmaceutical Biotechnology Joint Stock Company (JSC). The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- WHO . WHO Coronavirus Dashboard. (2021). Available at: https://covid19.who.int
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

