Untapped potential of physiology, behaviour and immune markers to predict range dynamics and marginality
- PMID: 34938448
- PMCID: PMC8668750
- DOI: 10.1002/ece3.8331
Untapped potential of physiology, behaviour and immune markers to predict range dynamics and marginality
Abstract
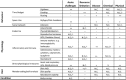
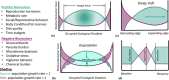
Linking environmental conditions to the modulators of individual fitness is necessary to predict long-term population dynamics, viability, and resilience. Functional physiological, behavioral, and reproductive markers can provide this mechanistic insight into how individuals perceive physiological, psychological, chemical, and physical environmental challenges through physiological and behavioral responses that are fitness proxies. We propose a Functional Marginality framework where relative changes in allostatic load, reproductive health, and behavior can be scaled up to evidence and establish causation of macroecological processes such as local extirpation, colonization, population dynamics, and range dynamics. To fully exploit functional traits, we need to move beyond single biomarker studies to develop an integrative approach that models the interactions between extrinsic challenges, physiological, and behavioral pathways and their modulators. In addition to providing mechanistic markers of range dynamics, this approach can also serve as a valuable conservation tool for evaluating individual- and population-level health, predicting responses to future environmental change and measuring the impact of interventions. We highlight specific studies that have used complementary biomarkers to link extrinsic challenges to population performance. These frameworks of integrated biomarkers have untapped potential to identify causes of decline, predict future changes, and mitigate against future biodiversity loss.
Keywords: conservation; endocrinology; glucocorticoids; gut health; macrophysiology; microbiome; social networks; thyroid hormone.
© 2021 The Authors. Ecology and Evolution published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare there are no conflicts of interest associated with this article.
Figures

References
-
- Amato, K. R. , Yeoman, C. J. , Kent, A. , Righini, N. , Carbonero, F. , Estrada, A. , Rex Gaskins, H. , Stumpf, R. M. , Yildirim, S. , Torralba, M. , Gillis, M. , Wilson, B. A. , Nelson, K. E. , White, B. A. , & Leigh, S. R. (2013). Habitat degradation impacts black howler monkey (Alouatta pigra) gastrointestinal microbiomes. The ISME Journal, 7, 1344–1353. 10.1038/ismej.2013.16 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bahnak, B. R. , Holland, J. C. , Verme, L. J. , & Ozoga, J. J. (1981). Seasonal and nutritional influences on growth hormone and thyroid activity in white‐tailed deer. The Journal of Wildlife Management, 45, 140–147. 10.2307/3807882 - DOI
-
- Bassett, B. L. , Hostetler, J. A. , Leone, E. , Shea, C. P. , Barbeau, B. D. , Lonati, G. L. , Panike, A. L. , Honaker, A. , & Ward‐Geiger, L. I. (2020). Quantifying sublethal Florida manatee watercraft interactions by examining scars on manatee carcasses. Endangered Species Research, 43, 395–408. 10.3354/esr01075 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

