Hot saline irrigation in comparison to nasal packing after sinus surgery
- PMID: 34938861
- PMCID: PMC8665458
- DOI: 10.1002/lio2.696
Hot saline irrigation in comparison to nasal packing after sinus surgery
Abstract
Objectives: Previous studies have shown that hot saline solution (HSS) nasal irrigation is effective against nasal bleeding and is used to treat nasal hemorrhage. In a pilot study, we evaluated hot saline nasal irrigation in comparison to a routinely used nasal packing in terms of self-reported complications and mucosal healing after functional endoscopic sinus surgery.
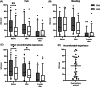
Methods: Patients undergoing surgery for bilateral chronic rhinosinusitis received polyvinyl acetate (PVA) nasal packing in the left nostril, and the right nostril was rinsed with 47°C sterile saline immediately after surgery. Patients' experiences of pain, bleeding, and other types of uncomfortable experiences were measured using a visual analog scale for each nostril before, during, and immediately after nasal packing removal. Two weeks post-surgery, the assessments were repeated including an endoscopic evaluation of the mucosa by the surgeon.
Results: Twenty-seven patients completed the study. Prior to removal of the packing, the patients experienced significantly more pain and other uncomfortable experiences in the nostril treated with nasal packing, as compared to the nostril solely rinsed with hot saline. After removal, patients reported significantly more uncomfortable experiences from the packing treated nostril. Two weeks post-surgery, no difference in mucosal healing was observed between the two nostrils.
Conclusions: The results from this study indicate that irrigation with HSS could be an alternative postoperative treatment to conventional PVA nasal packing. Hot saline irrigation may contribute to patients experiencing improved control of postoperative bleeding, pain, and less suffering of other causes as well as health-economic benefits, without affecting the mucosal healing up to 2 weeks post-surgery.
Level of evidence: 1b.
Keywords: chronic rhinosinusitis; endoscopic sinus surgery; hot saline; nonabsorbable packing; postoperative complications.
© 2021 The Authors. Laryngoscope Investigative Otolaryngology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Triological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Randomized controlled trial of steroid-soaked absorbable calcium alginate nasal packing following endoscopic sinus surgery.Laryngoscope. 2018 Feb;128(2):311-316. doi: 10.1002/lary.26871. Epub 2017 Sep 22. Laryngoscope. 2018. PMID: 28940582 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Guardcel Nasal Packing After Endoscopic Sinus Surgery: A Prospective, Single-Blind, Randomized Controlled Study.Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2017 Sep;10(3):248-253. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2016.01081. Epub 2016 Nov 17. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2017. PMID: 27927009 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy of cotton ball packing after endoscopic sinus surgery: A prospective, randomized, controlled trial.Auris Nasus Larynx. 2019 Oct;46(5):742-747. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2019.01.013. Epub 2019 Feb 17. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2019. PMID: 30782399 Clinical Trial.
-
Tranexamic acid for the reduction of bleeding during functional endoscopic sinus surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Feb 21;2(2):CD012843. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012843.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36808096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Practice Guideline: Nosebleed (Epistaxis) Executive Summary.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Jan;162(1):8-25. doi: 10.1177/0194599819889955. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020. PMID: 31910122 Review.
Cited by
-
The nomogram for predicting nasal bleeding after endoscopic transsphenoidal resection of pituitary adenomas: a retrospective study.Front Surg. 2024 Jul 19;11:1409298. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2024.1409298. eCollection 2024. Front Surg. 2024. PMID: 39100727 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dietz de Loos D, Lourijsen ES, Wildeman MAM, et al. Prevalence of chronic rhinosinusitis in the general population based on sinus radiology and symptomatology. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019;143(3):1207‐1214. - PubMed
-
- Hoehle LP, Phillips KM, Bergmark RW, Caradonna DS, Gray ST, Sedaghat AR. Symptoms of chronic rhinosinusitis differentially impact general health‐related quality of life. Rhinology. 2016;54(4):316‐322. - PubMed
-
- Dudvarski Z, Djukic V, Janosevic L, Tomanovic N, Soldatovic I. Influence of asthma on quality of life and clinical characteristics of patients with nasal polyposis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2013;270(4):1379‐1383. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
