KDM4B promotes acute myeloid leukemia associated with AML1-ETO by regulating chromatin accessibility
- PMID: 34938963
- PMCID: PMC8664044
- DOI: 10.1096/fba.2021-00030
KDM4B promotes acute myeloid leukemia associated with AML1-ETO by regulating chromatin accessibility
Abstract
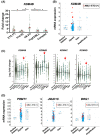
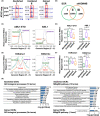
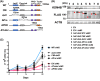
Epigenetic alterations of chromatin structure affect chromatin accessibility and collaborate with genetic alterations in the development of cancer. Lysine demethylase 4B (KDM4B) has been identified as a JmjC domain-containing epigenetic modifier that possesses histone demethylase activity. Although recent studies have demonstrated that KDM4B positively regulates the pathogenesis of multiple types of solid tumors, the tissue specificity and context dependency have not been fully elucidated. In this study, we investigated gene expression profiles established from clinical samples and found that KDM4B is elevated specifically in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) associated with chromosomal translocation 8;21 [t(8;21)], which results in a fusion of the AML1 and the eight-twenty-one (ETO) genes to generate a leukemia oncogene, AML1-ETO fusion transcription factor. Short hairpin RNA-mediated KDM4B silencing significantly reduced cell proliferation in t(8;21)-positive AML cell lines. Meanwhile, KDM4B silencing suppressed the expression of AML1-ETO-inducible genes, and consistently perturbed chromatin accessibility of AML1-ETO-binding sites involving altered active enhancer marks and functional cis-regulatory elements. Notably, transduction of murine KDM4B orthologue mutants followed by KDM4B silencing demonstrated a requirement of methylated-histone binding modules for a proliferative surge. To address the role of KDM4B in leukemia development, we further generated and analyzed Kdm4b conditional knockout mice. As a result, Kdm4b deficiency attenuated clonogenic potential mediated by AML1-ETO and delayed leukemia progression in vivo. Thus, our results highlight a tumor-promoting role of KDM4B in AML associated with t(8;21).
Keywords: acute myeloid leukemia; chromatin accessibility; gene expression analysis; gene targeting.
©2021 The Authors FASEB BioAdvances published by The Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Epigenetic Silencing of Eyes Absent 4 Gene by Acute Myeloid Leukemia 1-Eight-twenty-one Oncoprotein Contributes to Leukemogenesis in t(8;21) Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Chin Med J (Engl). 2016 Jun 5;129(11):1355-62. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.182838. Chin Med J (Engl). 2016. PMID: 27231175 Free PMC article.
-
AML1-ETO triggers epigenetic activation of early growth response gene l, inducing apoptosis in t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia.FEBS J. 2014 Feb;281(4):1123-31. doi: 10.1111/febs.12673. Epub 2014 Jan 10. FEBS J. 2014. PMID: 24314118
-
A novel AML1-ETO/FTO positive feedback loop promotes leukemogenesis and Ara-C resistance via stabilizing IGFBP2 in t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2024 Jan 24;13(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s40164-024-00480-z. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38268050 Free PMC article.
-
AML1/ETO and its function as a regulator of gene transcription via epigenetic mechanisms.Oncogene. 2021 Sep;40(38):5665-5676. doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-01952-w. Epub 2021 Jul 30. Oncogene. 2021. PMID: 34331016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The AML1 gene: a transcription factor involved in the pathogenesis of myeloid and lymphoid leukemias.Haematologica. 1997 May-Jun;82(3):364-70. Haematologica. 1997. PMID: 9234595 Review.
Cited by
-
KDM4B: A promising oncology therapeutic target.Cancer Sci. 2024 Jan;115(1):8-16. doi: 10.1111/cas.16005. Epub 2023 Nov 3. Cancer Sci. 2024. PMID: 37923555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KDM4B modulates autocrine IL6 in erythroblasts to prevent ineffective erythropoiesis.Leukemia. 2025 May;39(5):1228-1242. doi: 10.1038/s41375-025-02559-w. Epub 2025 Mar 12. Leukemia. 2025. PMID: 40074853
-
Methylation of the JMJD2B epigenetic regulator differentially affects its ability to coactivate the ETV1 and JUN transcription factors.Int J Biochem Mol Biol. 2023 Dec 15;14(6):101-115. eCollection 2023. Int J Biochem Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 38213775 Free PMC article.
-
FANCA deficiency promotes leukaemic progression by allowing the emergence of cells carrying oncogenic driver mutations.Oncogene. 2023 Sep;42(37):2764-2775. doi: 10.1038/s41388-023-02800-9. Epub 2023 Aug 12. Oncogene. 2023. PMID: 37573408 Free PMC article.
-
HIF1α-mediated transactivation of WTAP promotes AML cell proliferation via m6A-dependent stabilization of KDM4B mRNA.Leukemia. 2023 Jun;37(6):1254-1267. doi: 10.1038/s41375-023-01904-1. Epub 2023 Apr 22. Leukemia. 2023. PMID: 37087529
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
