Which Role Plays 2-Hydroxybutyric Acid on Insulin Resistance?
- PMID: 34940595
- PMCID: PMC8703345
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo11120835
Which Role Plays 2-Hydroxybutyric Acid on Insulin Resistance?
Abstract
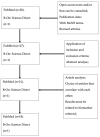
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2D) is defined as a chronic condition caused by beta cell loss and/or dysfunction and insulin resistance (IR). The discovering of novel biomarkers capable of identifying T2D and other metabolic disorders associated with IR in a timely and accurate way is critical. In this review, 2-hydroxybutyric acid (2HB) is presented as that upheaval biomarker with an unexplored potential ahead. Due to the activation of other metabolic pathways during IR, 2HB is synthesized as a coproduct of protein metabolism, being the progression of IR intrinsically related to the increasing of 2HB levels. Hence, the focus of this review will be on the 2HB metabolite and its involvement in glucose homeostasis. A literature review was conducted, which comprised an examination of publications from different databases that had been published over the previous ten years. A total of 19 articles fulfilled the intended set of criteria. The use of 2HB as an early indicator of IR was separated into subjects based on the number of analytes examined simultaneously. In terms of the association between 2HB and IR, it has been established that increasing 2HB levels can predict the development of IR. Thus, 2HB has demonstrated considerable promise as a clinical monitoring molecule, not only as an IR biomarker, but also for disease follow-up throughout IR treatment.
Keywords: 2-hydroxybutyric acid; impaired glucose tolerance; insulin resistance; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- International Diabetes Federation Atlas . 463 People Living with Diabetes Million. The International Diabetes Federation; Brussels, Belgium: 2019.
-
- Varvel S.A., Pottala J.V., Thiselton D.L., Caffrey R., Dall T., Sasinowski M., McConnell J.P., Warnick G.R., Voros S., Graham T.E. Serum α-hydroxybutyrate (α-HB) predicts elevated 1 h glucose levels and early-phase β-cell dysfunction during OGTT. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care. 2014;2:e000038. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2014-000038. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

