Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Fucoidan Extracts In Vitro
- PMID: 34940701
- PMCID: PMC8704339
- DOI: 10.3390/md19120702
Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Fucoidan Extracts In Vitro
Abstract
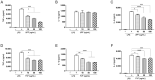
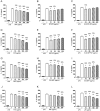
Fucoidans are sulfated, complex, fucose-rich polymers found in brown seaweeds. Fucoidans have been shown to have multiple bioactivities, including anti-inflammatory effects, and are known to inhibit inflammatory processes via a number of pathways such as selectin blockade and enzyme inhibition, and have demonstrated inhibition of inflammatory pathologies in vivo. In this current investigation, fucoidan extracts from Undaria pinnatifida, Fucus vesiculosus, Macrocystis pyrifera, Ascophyllum nodosum, and Laminaria japonica were assessed for modulation of pro-inflammatory cytokine production (TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6) by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and in a human macrophage line (THP-1). Fucoidan extracts exhibited no signs of cytotoxicity in THP-1 cells after incubation of 48 h. Additionally, all fucoidan extracts reduced cytokine production in LPS stimulated PBMCs and human THP-1 cells in a dose-dependent fashion. Notably, the 5-30 kDa subfraction from Macrocystis pyrifera was a highly effective inhibitor at lower concentrations. Fucoidan extracts from all species had significant anti-inflammatory effects, but the lowest molecular weight subfractions had maximal effects at low concentrations. These observations on various fucoidan extracts offer insight into strategies that improve their efficacy against inflammation-related pathology. Further studies should be conducted to elucidate the mechanism of action of these extracts.
Keywords: Ascophyllum nodosum; Fucus vesiculosus; Laminaria japonica; Macrocystis pyrifera; PBMCs; THP-1; TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6; Undaria pinnatifida; fucoidan.
Conflict of interest statement
The current study was sponsored by Marinova Pty. Ltd. (Cambridge, TAS, Australia) A.Y.P., S.S.K. and D.N.S. are employees of Marinova Pty. Ltd.
Figures
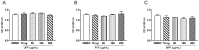

References
-
- Senthilkumar K., Kim S.-K. Chapter 11—Anticancer Effects of Fucoidan. In: Kim S.-K., editor. Advances in Food and Nutrition Research. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 2014. pp. 195–213. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

