HTR for Greek Historical Handwritten Documents
- PMID: 34940727
- PMCID: PMC8704904
- DOI: 10.3390/jimaging7120260
HTR for Greek Historical Handwritten Documents
Abstract
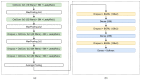
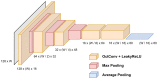
Offline handwritten text recognition (HTR) for historical documents aims for effective transcription by addressing challenges that originate from the low quality of manuscripts under study as well as from several particularities which are related to the historical period of writing. In this paper, the challenge in HTR is related to a focused goal of the transcription of Greek historical manuscripts that contain several particularities. To this end, in this paper, a convolutional recurrent neural network architecture is proposed that comprises octave convolution and recurrent units which use effective gated mechanisms. The proposed architecture has been evaluated on three newly created collections from Greek historical handwritten documents that will be made publicly available for research purposes as well as on standard datasets like IAM and RIMES. For evaluation we perform a concise study which shows that compared to state of the art architectures, the proposed one deals effectively with the challenging Greek historical manuscripts.
Keywords: convolutional neural networks; document image dataset; gated recurrent unit; handwritten text recognition; recurrent neural networks.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures










References
-
- De Sousa Neto A.F., Bezerra B.L.D., Toselli A.H., Lima E.B. HTR-Flor++: A Handwritten Text Recognition System Based on a Pipeline of Optical and Language Models; Proceedings of the DocEng ’20: ACM Symposium on Document Engineering 2020; Virtual Event. 29 September–1 October 2020; pp. 17:1–17:4. - DOI
-
- Puigcerver J. Are Multidimensional Recurrent Layers Really Necessary for Handwritten Text Recognition?; Proceedings of the 14th IAPR International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition; Kyoto, Japan. 9–15 November 2017; pp. 67–72. - DOI
-
- Chen Y., Fan H., Xu B., Yan Z., Kalantidis Y., Rohrbach M., Yan S., Feng J. Drop an Octave: Reducing Spatial Redundancy in Convolutional Neural Networks with Octave Convolution; Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision; Seoul, Korea. 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 3434–3443. - DOI
-
- Markou K., Tsochatzidis L.T., Zagoris K., Papazoglou A., Karagiannis X., Symeonidis S., Pratikakis I. A Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network for the Handwritten Text Recognition of Historical Greek Manuscripts; Proceedings of the Pattern Recognition, ICPR International Workshops and Challenges; Virtual Event. 10–15 January 2021; pp. 249–262. - DOI
-
- Marti U., Bunke H. The IAM-database: An English sentence database for offline handwriting recognition. Int. J. Doc. Anal. Recognit. 2002;5:39–46. doi: 10.1007/s100320200071. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

