A novel and unique ATP hydrolysis to AMP by a human Hsp70 Binding immunoglobin protein (BiP)
- PMID: 34941000
- PMCID: PMC8927878
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.4267
A novel and unique ATP hydrolysis to AMP by a human Hsp70 Binding immunoglobin protein (BiP)
Abstract
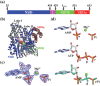
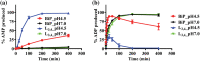
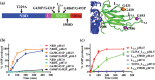
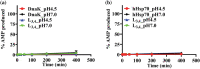
Hsp70s are ubiquitous and highly conserved molecular chaperones. They play crucial roles in maintaining cellular protein homeostasis. It is well established that Hsp70s use the energy of ATP hydrolysis to ADP to power the chaperone activity regardless of the cellular locations and isoforms. Binding immunoglobin protein (BiP), the major member of Hsp70s in the endoplasmic reticulum, is essential for protein folding and quality control. Unexpectedly, our structural analysis of BiP demonstrated a novel ATP hydrolysis to AMP during crystallization under the acidic conditions. Our biochemical studies confirmed this newly discovered ATP to AMP hydrolysis in solutions. Unlike the canonical ATP to ADP hydrolysis observed for Hsp70s, this ATP hydrolysis to AMP depends on the substrate-binding domain of BiP and is inhibited by the binding of a peptide substrate. Intriguingly, this ATP to AMP hydrolysis is unique to BiP, not shared by two representative Hsp70 proteins from the cytosol. Taken together, this novel and unique ATP to AMP hydrolysis may provide a potentially new direction for understanding the activity and cellular function of BiP.
Keywords: ADP; AMP; ATP; ATPase; BiP; Hsp70; heat shock proteins (HSPs); molecular chaperones; protein folding.
© 2021 The Protein Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

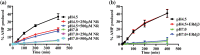
References
-
- Brodsky JL, Chiosis G. Hsp70 molecular chaperones: Emerging roles in human disease and identification of small molecule modulators. Curr Top Med Chem. 2006;6:1215–1225. - PubMed
-
- Rosenzweig R, Nillegoda NB, Mayer MP, Bukau B. The Hsp70 chaperone network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20:665–680. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

