Effect of a multi-disciplinary active aging intervention among community elders
- PMID: 34941126
- PMCID: PMC8701881
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000028314
Effect of a multi-disciplinary active aging intervention among community elders
Abstract
Background: Active aging has been the paradigm of the old-age lifestyle. We aimed to investigate the efficacy of a multi-disciplinary intervention program in community-based elderly.
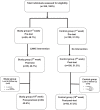
Methods: We conducted a 2-arm trial comparing the effectiveness between the study group and the control group. The intervention contents included active aging concepts and preparation, physical activity, health care management, cognitive training, emotional awareness and coping skills, family relationship and resilience, and internet use. A questionnaire tapping into the constructs of the expanded healthy life, mental health, social participation, and active aging was administered at baseline, 7th week, and 19th week.
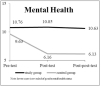
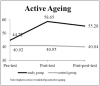
Results: The generalized estimating equations analysis revealed that the study group exhibited significant improvements in healthy life, mental health, social participation, and active aging compared with the control group (P < .001).
Conclusions: This study provided a good evidence supporting the effectiveness of a multi-disciplinary intervention program in improving the cognition of healthy life, mental health status, social participation activities, and active aging. A promotion of similar intervention is recommended.
Copyright © 2021 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Griffith TD. The relationship between death awareness and successful aging among older adults [Dissertation]. The Florida State University. ProQuest Dissertations Publishing 2001; 3026437.
-
- von Faber M, Bootsma-van der Wiel A, van Exel E, et al. Successful aging in the oldest old: Who can be characterized as successfully aged? Arch Intern Med 2001;161:2694–700. - PubMed
-
- Garfein AJ, Herzog AR. Robust aging among the young-old, old-old, and oldest-old. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci 1995;50:S77–87. - PubMed
-
- Active Ageing: A Policy Framework. WHO, 2002. Available at: http://www.who.int/ageing/publications/active/en/index.Html. Accessed November 30, 2010.
-
- Global Age-friendly Cities: A Guide. WHO, 2007. Available at: http://www.who.int/ageing/publications/Global_age_friendly_cities_Guide_.... AAccessed on November 30, 2010.

