A phase 2a clinical trial of molnupiravir in patients with COVID-19 shows accelerated SARS-CoV-2 RNA clearance and elimination of infectious virus
- PMID: 34941423
- PMCID: PMC10763622
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abl7430
A phase 2a clinical trial of molnupiravir in patients with COVID-19 shows accelerated SARS-CoV-2 RNA clearance and elimination of infectious virus
Abstract
There is an urgent need for an effective, oral, direct-acting therapeutic to block transmission of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and prevent progression to severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). In a phase 2a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized, multicenter clinical trial, we evaluated the safety, tolerability, and antiviral efficacy of the nucleoside analog molnupiravir in 202 unvaccinated participants with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection and symptom duration <7 days. Participants were randomized 1:1 to receive molnupiravir (200 mg) or placebo and then 3:1 to receive molnupiravir (400 or 800 mg) or placebo, orally twice daily for 5 days. Antiviral activity was assessed by reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) for SARS-CoV-2 RNA in nasopharyngeal swabs. Infectious virus was assessed by inoculation of cultured Vero cells with samples from nasopharyngeal swabs and was detected by RT-PCR. Time to viral RNA clearance (primary endpoint) was decreased in the 800-mg molnupiravir group (median 14 days) compared to the placebo group (median 15 days) (log rank P value = 0.013). Of participants receiving 800 mg of molnupiravir, 92.5% achieved viral RNA clearance compared with 80.3% of placebo recipients by study end (4 weeks). Infectious virus (secondary endpoint) was detected in swabs from 1.9% of the 800-mg molnupiravir group compared with 16.7% of the placebo group at day 3 of treatment (P = 0.016). At day 5 of treatment, infectious virus was not isolated from any participants receiving 400 or 800 mg of molnupiravir compared with 11.1% of placebo recipients (P = 0.034 and 0.027, respectively). Molnupiravir was well tolerated across all doses.
Figures
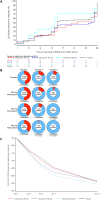
Update of
-
Molnupiravir, an Oral Antiviral Treatment for COVID-19.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2021 Jun 17:2021.06.17.21258639. doi: 10.1101/2021.06.17.21258639. medRxiv. 2021. Update in: Sci Transl Med. 2022 Jan 19;14(628):eabl7430. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abl7430. PMID: 34159342 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- World Health Organisation. Weekly epidemiological update on COVID-19. Edition 70, published 14 December 2021.– [Internet]. Coronavirus Dis. COVID-19 Pandemic. [cited 2021 Dec 14]; https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on....
-
- Chen P., Nirula A., Heller B., Gottlieb R. L., Boscia J., Morris J., Huhn G., Cardona J., Mocherla B., Stosor V., Shawa I., Adams A. C., Van Naarden J., Custer K. L., Shen L., Durante M., Oakley G., Schade A. E., Sabo J., Patel D. R., Klekotka P., Skovronsky D. M.; BLAZE-1 Investigators , SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody LY-CoV555 in outpatients with COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 384, 229–237 (2021). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wölfel R., Corman V. M., Guggemos W., Seilmaier M., Zange S., Müller M. A., Niemeyer D., Jones T. C., Vollmar P., Rothe C., Hoelscher M., Bleicker T., Brünink S., Schneider J., Ehmann R., Zwirglmaier K., Drosten C., Wendtner C., Author correction: Virological assessment of hospitalized patients with COVID-2019. Nature 588, E35–E35 (2020). - PubMed
-
- van Kampen J. J. A., van de Vijver D. A. M. C., Fraaij P. L. A., Haagmans B. L., Lamers M. M., Okba N., van den Akker J. P. C., Endeman H., Gommers D. A. M. P. J., Cornelissen J. J., Hoek R. A. S., van der Eerden M. M., Hesselink D. A., Metselaar H. J., Verbon A., de Steenwinkel J. E. M., Aron G. I., van Gorp E. C. M., van Boheemen S., Voermans J. C., Boucher C. A. B., Molenkamp R., Koopmans M. P. G., Geurtsvankessel C., van der Eijk A. A., Duration and key determinants of infectious virus shedding in hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19). Nat. Commun. 12, 267 (2021). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

