Safety and Immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines in Patients With Chronic Liver Diseases (CHESS-NMCID 2101): A Multicenter Study
- PMID: 34942370
- PMCID: PMC8686447
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.12.022
Safety and Immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines in Patients With Chronic Liver Diseases (CHESS-NMCID 2101): A Multicenter Study
Abstract
Background & aims: We aimed to assess the safety and immunogenicity of inactivated whole-virion severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) vaccines in patients with chronic liver diseases (CLD) in this study.
Methods: This was a prospective, multi-center, open-label study. Participants aged over 18 years with confirmed CLD and healthy volunteers were enrolled. All participants received 2 doses of inactivated whole-virion SARS-CoV-2 vaccines. Adverse reactions were recorded within 14 days after any dose of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, laboratory testing results were collected after the second dose, and serum samples of enrolled subjects were collected and tested for SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies at least 14 days after the second dose.
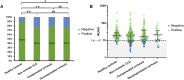
Results: A total of 581 participants (437 patients with CLD and 144 healthy volunteers) were enrolled from 15 sites in China. Most adverse reactions were mild and transient, and injection site pain (n = 36; 8.2%) was the most frequently reported adverse event. Three participants had grade 3 aminopherase elevation (defined as alanine aminopherase >5 upper limits of normal) after the second dose of inactivated whole-virion SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, and only 1 of them was judged as severe adverse event potentially related to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination. The positive rates of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies were 76.8% in the noncirrhotic CLD group, 78.9% in the compensated cirrhotic group, 76.7% in the decompensated cirrhotic group (P = .894 among CLD subgroups), and 90.3% in healthy controls (P = .008 vs CLD group).
Conclusion: Inactivated whole-virion SARS-CoV-2 vaccines are safe in patients with CLD. Patients with CLD had lower immunologic response to SARS-CoV-2 vaccines than healthy population. The immunogenicity is similarly low in noncirrhotic CLD, compensated cirrhosis, and decompensated cirrhosis.
Keywords: Chronic Liver Diseases; Cirrhosis; Immunogenicity; SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines; Safety.
Copyright © 2022 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Poor Response to Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine in Patients With Chronic Liver Disease.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Aug;20(8):1892-1893. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2022.01.029. Epub 2022 Feb 3. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35123090 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organiztion coronavirus (COVID-19) dashboard. https://covid19.who.int/ Available at: . Accessed October 1, 2021.
-
- Younossi Z., Anstee Q.M., Marietti M., et al. Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;15:11–20. - PubMed
-
- Asrani S.K., Devarbhavi H., Eaton J., et al. Burden of liver diseases in the world. J Hepatol. 2019;70:151–171. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization hepatitis topics. https://www.who.int/health-topics/hepatitis#tab=tab_1 Available at:
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

