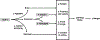Semaglutide for the treatment of obesity
- PMID: 34942372
- PMCID: PMC9209591
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcm.2021.12.008
Semaglutide for the treatment of obesity
Abstract
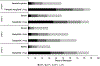
Semaglutide is a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist that was recently approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for chronic weight management. This paper reviews data on the mechanism of action, weight-loss and cardiometabolic efficacy, and safety of semaglutide 2.4 mg/week for obesity. Semaglutide has demonstrated the largest weight loss of any obesity medication to date with reductions of approximately 15% of initial weight at 68 weeks, accompanied by improvements in cardiovascular risks factors and physical functioning. The approval of this medication provides patients with greater options for weight management.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Editorial commentary: Weight loss for cardiovascular disease prevention - is semaglutide the answer?Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Apr;33(3):167-169. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2021.12.018. Epub 2022 Jan 5. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 34999021 No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Obesity and overweight 2018. [Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight.
-
- Ortega FB, Lavie CJ, Blair SN. Obesity and cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. 2016;118(11):1752–70. - PubMed
-
- Aggarwal R, Vaduganathan M, Chiu N, Bhatt DL. Potential implications of the FDA approval of semaglutide for overweight and obese adults in the United States. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2021. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical