Increased Kynurenine Indicates a Fatal Course of COVID-19
- PMID: 34943063
- PMCID: PMC8750518
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox10121960
Increased Kynurenine Indicates a Fatal Course of COVID-19
Abstract
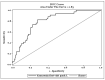
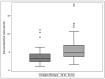
(1) Background: An inefficient immune response accompanied by an overwhelming inflammatory reaction is involved in severe courses of COVID-19. Kynurenine (KYN) has important immune-modulatory functions and may contribute to a failure in controlling SARS-CoV-2. The present study aims to explore biomarkers that hint at a fatal outcome of COVID-19 early on. (2) Methods: We established a cohort of 148 hospitalized COVID-19 patients for this study. Thirty-one patients died due to a severe COVID-19 course, and 117 recovered within 90 days. We built a biobank by collecting left-over material from these patients whenever blood arrived at the central laboratory of our University hospital for analysis of routine markers. The scientific laboratory analysis comprised KYN, Tryptophan (TRP), KYN/TRP ratio, ferritin, interleukin-6 (IL-6), C-reactive protein (CRP), creatinine, N-terminal pro-natriuretic peptide (NTproBNP), troponin T (TnT), fibrinogen, D-Dimer, prothrombin time (PT), activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), antithrombin (AT), protein C, protein S, factor XIII, lupus aPTT, angiotensin-2, vitamin D metabolites, and telomeres in all COVID-19 patients. Basic clinical characteristics and anteceding diseases including cardiovascular, oncologic, renal, hypertension, pulmonary, metabolic (diabetes, obesity) were recorded in a database together with the laboratory data. (3) Results: At the time of diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection those patients who deceased within 90 days afterwards due to COVID-19, had a significantly higher age, higher KYN, KYN/TRP ratio, ferritin, creatinine, and NTproBNP values than SARS-CoV-2 patients who survived COVID-19 along the same time span. In a Kaplan-Meier analysis the variables age, KYN, ferritin, D-Dimer, TnT, NTproBNP, and creatinine showed a significant influence on survival time. Gender, however, showed no influence. In a combined Cox regression analysis KYN had the highest hazard ratio (1.188, 95% CI: 1.071-1.319) followed by age (1.041, 95% CI: 1.011-1.073). In a ROC analysis, KYN values above the cut off limit of 4.82 nmol/l (as specified by Youden index) had a sensitivity of 82% (95% CI: 66-95%) and a specificity of 72% (95% CI: 65-82%) to predict COVID-19 related death within 90 days observation time. (4) Conclusions: Kynurenine is a promising blood biomarker to predict an increased risk of mortality in SARS-CoV-2 infected people already at the time of the first positive SARS-CoV-2 verification detected in these persons.
Keywords: COVID-19; kynurenine; tryptophan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Reyes Ocampo J., Lugo Huitron R., Gonzalez-Esquivel D., Ugalde-Muniz P., Jimenez-Anguiano A., Pineda B., Pedraza-Chaverri J., Rios C., Perez de la Cruz V. Kynurenines with neuroactive and redox properties: Relevance to aging and brain diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2014;2014:646909. doi: 10.1155/2014/646909. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Niinisalo P., Raitakari O.T., Kahonen M., Hurme M., Lehtimaki T., Magnussen C., Viikari J., Juonala M., Kaaja R. IDO activity forecasts obesity in males and premenopausal females in a 10-year follow-up study: The Cardiovascular Risk in Young Finns Study. Atherosclerosis. 2021;336:32–38. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2021.09.018. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nguyen N.T., Kimura A., Nakahama T., Chinen I., Masuda K., Nohara K., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Kishimoto T. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor negatively regulates dendritic cell immunogenicity via a kynurenine-dependent mechanism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2010;107:19961–19966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1014465107. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous