Association of Infant Feeding Practices with Iron Status and Hematologic Parameters in 6-Month-Old Infants
- PMID: 34943355
- PMCID: PMC8700198
- DOI: 10.3390/children8121159
Association of Infant Feeding Practices with Iron Status and Hematologic Parameters in 6-Month-Old Infants
Abstract
Background: Infants' feeding practices in the first 6 months of life and their association with iron status and hematologic parameters has not been well studied. We aim to evaluate this association.
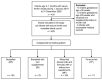
Methods: In a retrospective chart review, we identified 403 infants who received laboratory screening for anemia at 6-month visits. Infants were categorized into four groups according to feeding practices. Hematologic parameters and incidence of anemia, iron deficiency (ID), and iron deficiency anemia (IDA) were compared.
Results: In total, 105 infants were breastfed (BF), 78 were breastfed with iron supplementation starting at 4 months (BI), 109 were mixed-fed (breast milk and formula) with or without iron supplementation (MF), and 111 were formula-fed (FF). The BF group had the highest incidence of anemia (38.1%), ID (28.6%), and IDA (17.1%) when compared with the other groups (p < 0.001). In multivariate logistic regression, BI, MF, and FF infants had 90.4%, 97.5%, and 96.9% decreased risk of IDA, respectively, with BF infants as a reference group.
Conclusion: The incidence of anemia, ID, and IDA at age 6 months was higher in BF than FF or MF infants. However, iron supplements in BF infants starting at 4 months significantly reduced their ID and IDA incidence.
Keywords: breastfeeding; formula feeding; infant feeding; iron deficiency anemia; iron supplements.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Petry N., Olofin I., Hurrell R.F., Boy E., Wirth J.P., Moursi M., Donahue Angel M., Rohner F. The proportion of anemia associated with iron deficiency in low, medium, and high Human Development Index countries: A systematic analysis of national surveys. Nutrients. 2016;8:693. doi: 10.3390/nu8110693. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lozoff B., Brittenham G.M., Wolf A.W., McClish D.K., Kuhnert P.M., Jimenez E., Jimenez R., Mora L.A., Gomez I., Krauskoph D. Iron deficiency anemia and iron therapy effects on infant developmental test performance. Pediatrics. 1987;79:981–995. Correction in Pediatrics 1988, 81, 683. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous