VGG19 Network Assisted Joint Segmentation and Classification of Lung Nodules in CT Images
- PMID: 34943443
- PMCID: PMC8699868
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics11122208
VGG19 Network Assisted Joint Segmentation and Classification of Lung Nodules in CT Images
Abstract
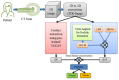
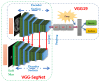
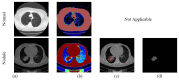
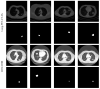
Pulmonary nodule is one of the lung diseases and its early diagnosis and treatment are essential to cure the patient. This paper introduces a deep learning framework to support the automated detection of lung nodules in computed tomography (CT) images. The proposed framework employs VGG-SegNet supported nodule mining and pre-trained DL-based classification to support automated lung nodule detection. The classification of lung CT images is implemented using the attained deep features, and then these features are serially concatenated with the handcrafted features, such as the Grey Level Co-Occurrence Matrix (GLCM), Local-Binary-Pattern (LBP) and Pyramid Histogram of Oriented Gradients (PHOG) to enhance the disease detection accuracy. The images used for experiments are collected from the LIDC-IDRI and Lung-PET-CT-Dx datasets. The experimental results attained show that the VGG19 architecture with concatenated deep and handcrafted features can achieve an accuracy of 97.83% with the SVM-RBF classifier.
Keywords: VGG-SegNet; deep learning; lung CT images; nodule detection; pre-trained VGG19.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







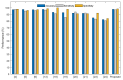
References
-
- WHO [(accessed on 21 September 2021)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer.
-
- Olson E.J. [(accessed on 21 September 2021)]. Available online: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/lung-cancer/expert-answer....
-
- Bhandary A., Prabhu G.A., Rajinikanth V., Thanaraj K.P., Satapathy S.C., Robbins D.E., Shasky C., Zhang Y.D., Tavares J.M.R.S., Raja N.S.M. Deep-learning framework to detect lung abnormality—A study with chest X-Ray and lung CT scan images. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2020;129:271–278. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2019.11.013. - DOI
-
- Choi W.J., Choi T.S. Automated pulmonary nodule detection system in computed tomography images: A hierarchical block classification approach. Entropy. 2013;15:507–523. doi: 10.3390/e15020507. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

