Performance of Spectral Photon-Counting Coronary CT Angiography and Comparison with Energy-Integrating-Detector CT: Objective Assessment with Model Observer
- PMID: 34943611
- PMCID: PMC8700425
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics11122376
Performance of Spectral Photon-Counting Coronary CT Angiography and Comparison with Energy-Integrating-Detector CT: Objective Assessment with Model Observer
Abstract
Aims: To evaluate spectral photon-counting CT's (SPCCT) objective image quality characteristics in vitro, compared with standard-of-care energy-integrating-detector (EID) CT.
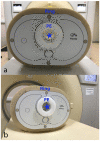
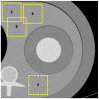
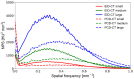
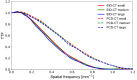
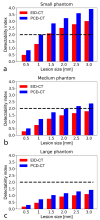
Methods: We scanned a thorax phantom with a coronary artery module at 10 mGy on a prototype SPCCT and a clinical dual-layer EID-CT under various conditions of simulated patient size (small, medium, and large). We used filtered back-projection with a soft-tissue kernel. We assessed noise and contrast-dependent spatial resolution with noise power spectra (NPS) and target transfer functions (TTF), respectively. Detectability indices (d') of simulated non-calcified and lipid-rich atherosclerotic plaques were computed using the non-pre-whitening with eye filter model observer.
Results: SPCCT provided lower noise magnitude (9-38% lower NPS amplitude) and higher noise frequency peaks (sharper noise texture). Furthermore, SPCCT provided consistently higher spatial resolution (30-33% better TTF10). In the detectability analysis, SPCCT outperformed EID-CT in all investigated conditions, providing superior d'. SPCCT reached almost perfect detectability (AUC ≈ 95%) for simulated 0.5-mm-thick non-calcified plaques (for large-sized patients), whereas EID-CT had lower d' (AUC ≈ 75%). For lipid-rich atherosclerotic plaques, SPCCT achieved 85% AUC vs. 77.5% with EID-CT.
Conclusions: SPCCT outperformed EID-CT in detecting simulated coronary atherosclerosis and might enhance diagnostic accuracy by providing lower noise magnitude, markedly improved spatial resolution, and superior lipid core detectability.
Keywords: cardiac imaging techniques; computed tomography angiography; coronary vessels; image quality enhancement; phantoms imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
Yoad Yagil, Klaus Erhard, and Elias Lahoud declare relationships with the following company: Philips Healthcare.
Figures


References
-
- Cavallo A.U., Patterson A.J., Thomas R., Alaiti M.A., Attizzani G.F., Laukamp K., Hokamp N.G., Bezerra H., Gilkeson R., Rajagopalan S. Low dose contrast CT for transcatheter aortic valve replacement assessment: Results from the prospective SPECTACULAR study (spectral CT assessment prior to TAVR) J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2020;14:68–74. doi: 10.1016/j.jcct.2019.06.015. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rotzinger D.C., Si-Mohamed S.A., Yerly J., Boccalini S., Becce F., Boussel L., Meuli R.A., Qanadli S.D., Douek P.C. Reduced-iodine-dose dual-energy coronary CT angiography: Qualitative and quantitative comparison between virtual monochromatic and polychromatic CT images. Eur. Radiol. 2021;31:7132–7142. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-07809-w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

