The Role of Serum Th1, Th2, and Th17 Cytokines in Patients with Alopecia Areata: Clinical Implications
- PMID: 34943905
- PMCID: PMC8699846
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10123397
The Role of Serum Th1, Th2, and Th17 Cytokines in Patients with Alopecia Areata: Clinical Implications
Abstract
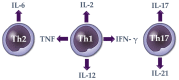
Alopecia areata is a type of non-scarring hair loss. The dysregulation of numerous systemic Th1 (IL-2, IFN-γ, TNF, IL-12, and IL-18), Th2 (IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-9, IL-10, IL-13, IL-17E, IL-31 and IL-33) and Th17 (IL-17, IL-17F, IL-21, IL-22, IL-23 and TGF-β) cytokines was observed in patients with alopecia areata. Positive correlations between the severity of alopecia areata and an increased serum level of various cytokines including IL-2, TNF, IL-12, IL-17, and IL-17E were reported in the literature. An increased serum level of numerous cytokines, such as IL-2, IL-6, TNF, IL-12, IL-17E, and IL-22, was described as positively correlated with the duration of the disease. Moreover, it was shown that increased pre-treatment serum level of IL-12 was a positive, while increased serum levels of IL-4 and IL-13 were negative prognostic markers for the efficacy of diphenylcyclopropenone. In conclusion, alopecia areata is associated with the dysregulation of systemic Th1, Th2 and Th17 cytokines with their role in the pathogenesis, clinical manifestations and prognosis of the disease. Available data indicate the most significant role of serum IL-2, TNF, IL-12, IL-17, and IL-17E as markers of disease activity. The serum levels IL-4, IL-12 and IL-13 may be useful as potential predictors of diphenylcyclopropenone efficacy.
Keywords: chemokine; cytokine; immunology; interleukin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Vano-Galvan S., Saceda-Corralo D., Blume-Peytavi U., Cucchia J., Dlova N.C., Gavazzoni Dias M.F.R., Grimalt R., Guzman-Sanchez D., Harries M., Ho A., et al. Frequency of the Types of Alopecia at Twenty-Two Specialist Hair Clinics: A Multicenter Study. Ski. Appendage Disord. 2019;5:309–315. doi: 10.1159/000496708. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous