The Nuts and Bolts of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor-Binding Domain Heterologous Expression
- PMID: 34944456
- PMCID: PMC8699011
- DOI: 10.3390/biom11121812
The Nuts and Bolts of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor-Binding Domain Heterologous Expression
Abstract
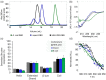
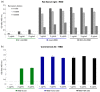
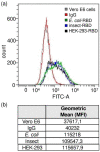
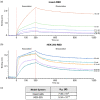
COVID-19 is a highly infectious disease caused by a newly emerged coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) that has rapidly progressed into a pandemic. This unprecedent emergency has stressed the significance of developing effective therapeutics to fight the current and future outbreaks. The receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the SARS-CoV-2 surface Spike protein is the main target for vaccines and represents a helpful "tool" to produce neutralizing antibodies or diagnostic kits. In this work, we provide a detailed characterization of the native RBD produced in three major model systems: Escherichia coli, insect and HEK-293 cells. Circular dichroism, gel filtration chromatography and thermal denaturation experiments indicated that recombinant SARS-CoV-2 RBD proteins are stable and correctly folded. In addition, their functionality and receptor-binding ability were further evaluated through ELISA, flow cytometry assays and bio-layer interferometry.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; heterologous expression; protein production; receptor-binding domain; spike protein.
Conflict of interest statement
Mariano Maffei, Grazia Vitagliano, Shaila Sellathurai, Federica Bucci, Alessia Muzi and Valerio Chiarini are employees of the companies Evvivax and Takis. Mirco Compagnone is an employee at NeoMatrix. Luigi Fedele is a former employee of the company Takis. Giuseppe Roscilli and Emanuele Marra are co-founders of the companies Takis and Evvivax. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Coronavirus. 2021. [(accessed on 27 October 2021)]. Available online: https://covid19.who.int.
-
- Tai W., He L., Zhang X., Pu J., Voronin D., Jiang S., Zhou Y., Du L. Characterization of the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implication for development of RBD protein as a viral attachment inhibitor and vaccine. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2020;17:613–620. doi: 10.1038/s41423-020-0400-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

