Animal Models in Bladder Cancer
- PMID: 34944577
- PMCID: PMC8698361
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines9121762
Animal Models in Bladder Cancer
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Constantin et al. Animal Models in Bladder Cancer. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1762.Biomedicines. 2022 Jan 6;10(1):110. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10010110. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35052877 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Bladder cancer (urothelial cancer of the bladder) is the most common malignancy affecting the urinary system with an increasing incidence and mortality. Mouse models of bladder cancer should possess a high value of reproducibility, predictability, and translatability to allow mechanistic, chemo-preventive, and therapeutic studies that can be furthered into human clinical trials.
Objectives: To provide an overview and resources on the origin, molecular and pathological characteristics of commonly used animal models in bladder cancer.
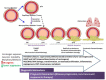
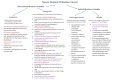
Methods: A PubMed and Web of Science search was performed for relevant articles published between 1980 and 2021 using words such as: "bladder" and/or "urothelial carcinoma" and animal models. Animal models of bladder cancer can be categorized as autochthonous (spontaneous) and non-autochthonous (transplantable). The first are either chemically induced models or genetically engineered models. The transplantable models can be further subclassified as syngeneic (murine bladder cancer cells implanted into immunocompetent or transgenic mice) and xenografts (human bladder cancer cells implanted into immune-deficient mice). These models can be further divided-based on the site of the tumor-as orthotopic (tumor growth occurs within the bladder) and heterotopic (tumor growth occurs outside of the bladder).
Keywords: animal models; bladder cancer; urothelial cancer; xenografts.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- De George K.C., Holt H.R., Hodges S.C. Bladder cancer: Diagnosis and Treatment. Am. Fam. Physician. 2017;96:507–514. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

