HSP90 Inhibition Synergizes with Cisplatin to Eliminate Basal-like Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Cells
- PMID: 34944784
- PMCID: PMC8699576
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13246163
HSP90 Inhibition Synergizes with Cisplatin to Eliminate Basal-like Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Cells
Abstract
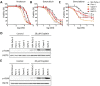
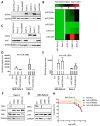
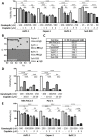
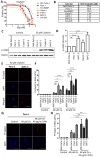
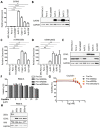
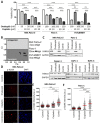
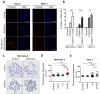
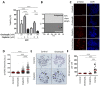
To improve the treatment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), a promising strategy consists of personalized chemotherapy based on gene expression profiles. Investigating a panel of PDAC-derived human cell lines, we found that their sensitivities towards cisplatin fall in two distinct classes. The platinum-sensitive class is characterized by the expression of GATA6, miRNA-200a, and miRNA-200b, which might be developable as predictive biomarkers. In the case of resistant PDAC cells, we identified a synergism of cisplatin with HSP90 inhibitors. Mechanistic explanations of this synergy include the degradation of Fanconi anemia pathway factors upon HSP90 inhibition. Treatment with the drug combination resulted in increased DNA damage and chromosome fragmentation, as we have reported previously for ovarian cancer cells. On top of this, HSP90 inhibition also enhanced the accumulation of DNA-bound platinum. We next investigated an orthotopic syngeneic animal model consisting of tumors arising from KPC cells (LSL-KrasG12D/+; LSL-Trp53R172H/+; Pdx-1-Cre, C57/BL6 genetic background). Here again, when treating established tumors, the combination of cisplatin with the HSP90 inhibitor onalespib was highly effective and almost completely prevented further tumor growth. We propose that the combination of platinum drugs and HSP90 inhibitors might be worth testing in the clinics for the treatment of cisplatin-resistant PDACs.
Keywords: HSP90 inhibition; PDAC; basal-like subtype; cisplatin; platinum-DNA adducts; synergism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Burris H.A., Moore M.J., Andersen J., Green M.R., Rothenberg M.L., Modiano M.R., Cripps M.C., Portenoy R.K., Storniolo A.M., Tarassoff P., et al. Improvements in survival and clinical benefit with gemcitabine as first-line therapy for patients with advanced pancreas cancer: A randomized trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 1997;15:2403–2413. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1997.15.6.2403. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jameson G.S., Borazanci E., Babiker H.M., Poplin E., Niewiarowska A.A., Gordon M.S., Barrett M.T., Rosenthal A., Stoll-D’Astice A., Crowley J., et al. Response Rate Following Albumin-Bound Paclitaxel Plus Gemcitabine Plus Cisplatin Treatment Among Patients with Advanced Pancreatic Cancer: A Phase 1b/2 Pilot Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020;6:125–132. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.3394. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

