RNA Biomarkers as a Response Measure for Survival in Patients with Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 34944897
- PMCID: PMC8699291
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13246279
RNA Biomarkers as a Response Measure for Survival in Patients with Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
Abstract
Treatment evaluation in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer is challenging. There is an urgent need for biomarkers to discriminate short-term survivors from long-term survivors, shortly after treatment initiation. Thereto, the added value of early RNA biomarkers on predicting progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were explored. The RNA biomarkers: KLK3 mRNA, miR-375, miR-3687, and NAALADL2-AS2 were measured in 93 patients with mCRPC, before and 1 month after start of first-line abiraterone acetate or enzalutamide treatment, in two prospective clinical trials. The added value of the biomarkers to standard clinical parameters in predicting PFS and OS was tested by Harell's C-index. To test whether the biomarkers were independent markers of PFS and OS, multivariate Cox regression was used. The best prediction model for PFS and OS was formed by adding miR-375 and KLK3 (at baseline and 1 month) to standard clinical parameters. Baseline miR-375 and detectable KLK3 after 1 month of therapy were independently related to shorter PFS, which was not observed for OS. In conclusion, the addition of KLK3 and miR-375 (at baseline and 1 month) to standard clinical parameters resulted in the best prediction model for survival assessment.
Keywords: RNA; abiraterone acetate; biomarkers; castration-resistant prostate cancer; enzalutamide; liquid biopsy; survival.
Conflict of interest statement
I.M.v.O.: Advisory role (compensated and institutional): Roche, Bayer, Astellas, Astra-Zeneca/MSD, select MDX and Janssen. Research support (institutional): Astellas, Janssen. Travel support: Astellas; D.M.S.: Astellas, Bayer, Besins, Janssen. P.H.: Consulting fees: Astellas, MSD, Pfizer AstraZeneca, BMS, Ipsen. N.P.E.: Astellas, Janssen-Cilag, Sanofi, Bayer; N.M.: Advisory role (compensated and institutional): Roche, MSD, BMS, Bayer, Astellas and Janssen. Research support (institutional): Astellas, Janssen, Pfizer, Roche and Sanofi Genzyme. Travel support: Astellas, MSD. J.A.S.: advisor MDx Health. J.A.S., G.W.V. and F.S. are inventors on the PCA3-related IP. The IP is owned by their employer, Radboud university medical center, which has licensed the technology and receives royalty payments. All remaining authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures
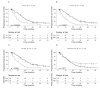
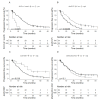
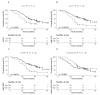
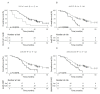
References
-
- Montgomery R.B., Mostaghel E.A., Vessella R., Hess D.L., Kalhorn T.F., Higano C.S., True L.D., Nelson P.S. Maintenance of intratumoral androgens in metastatic prostate cancer: A mechanism for castration-resistant tumor growth. Cancer Res. 2008;68:4447–4454. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-0249. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Scher H.I., Beer T.M., Higano C.S., Anand A., Taplin M.E., Efstathiou E., Rathkopf D., Shelkey J., Yu E.Y., Alumkal J., et al. Antitumour activity of MDV3100 in castration-resistant prostate cancer: A phase 1–2 study. Lancet. 2010;375:1437–1446. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60172-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Attard G., Reid A.H., Yap T.A., Raynaud F., Dowsett M., Settatree S., Barrett M., Parker C., Martins V., Folkerd E., et al. Phase I clinical trial of a selective inhibitor of CYP17, abiraterone acetate, confirms that castration-resistant prostate cancer commonly remains hormone driven. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2008;26:4563–4571. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.15.9749. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

