Liver-Directed Therapy for Neuroendocrine Metastases: From Interventional Radiology to Nuclear Medicine Procedures
- PMID: 34944988
- PMCID: PMC8699378
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13246368
Liver-Directed Therapy for Neuroendocrine Metastases: From Interventional Radiology to Nuclear Medicine Procedures
Abstract
Neuroendocrine neoplasms (NENs) are rare and heterogeneous epithelial tumors most commonly arising from the gastroenteropancreatic (GEP) system. GEP-NENs account for approximately 60% of all NENs, and the small intestine and pancreas represent two most common sites of primary tumor development. Approximately 80% of metastatic patients have secondary liver lesions, and in approximately 50% of patients, the liver is the only metastatic site. The therapeutic strategy depends on the degree of hepatic metastatic invasion, ranging from liver surgery or percutaneous ablation to palliative treatments to reduce both tumor volume and secretion. In patients with grade 1 and 2 NENs, locoregional nonsurgical treatments of liver metastases mainly include percutaneous ablation and endovascular treatments, targeting few or multiple hepatic metastases, respectively. In the present work, we provide a narrative review of the current knowledge on liver-directed therapy for metastasis treatment, including both interventional radiology procedures and nuclear medicine options in NEN patients, taking into account the patient clinical context and both the strengths and limitations of each modality.
Keywords: interventional radiology; liver metastasis; liver-directed therapy; neuroendocrine; nuclear medicine; radioembolization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

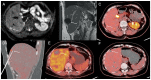
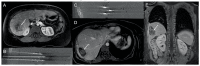


References
-
- Yao J.C., Hassan M.M., Phan A.T., Dagohoy C.G., Leary C.C., Mares J.E., Abdalla E.K., Fleming J.B., Vauthey J.-N., Rashid A., et al. One hundred years after “carcinoid”: Epidemiology of and prognostic factors for neuroendocrine tumors in 35,825 cases in the United States. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008;26:3063–3072. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.15.4377. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

