Emotional Intelligence Measures: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 34946422
- PMCID: PMC8701889
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare9121696
Emotional Intelligence Measures: A Systematic Review
Abstract
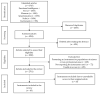
Emotional intelligence (EI) refers to the ability to perceive, express, understand, and manage emotions. Current research indicates that it may protect against the emotional burden experienced in certain professions. This article aims to provide an updated systematic review of existing instruments to assess EI in professionals, focusing on the description of their characteristics as well as their psychometric properties (reliability and validity). A literature search was conducted in Web of Science (WoS). A total of 2761 items met the eligibility criteria, from which a total of 40 different instruments were extracted and analysed. Most were based on three main models (i.e., skill-based, trait-based, and mixed), which differ in the way they conceptualize and measure EI. All have been shown to have advantages and disadvantages inherent to the type of tool. The instruments reported in the largest number of studies are Emotional Quotient Inventory (EQ-i), Schutte Self Report-Inventory (SSRI), Mayer-Salovey-Caruso Emotional Intelligence Test 2.0 (MSCEIT 2.0), Trait Meta-Mood Scale (TMMS), Wong and Law's Emotional Intelligence Scale (WLEIS), and Trait Emotional Intelligence Questionnaire (TEIQue). The main measure of the estimated reliability has been internal consistency, and the construction of EI measures was predominantly based on linear modelling or classical test theory. The study has limitations: we only searched a single database, the impossibility of estimating inter-rater reliability, and non-compliance with some items required by PRISMA.
Keywords: emotional intelligence; measure; questionnaire; scale; systematic review; test.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Similar articles
-
The Association Between Emotional Intelligence and Suicidal Behavior: A Systematic Review.Front Psychol. 2018 Nov 30;9:2380. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.02380. eCollection 2018. Front Psychol. 2018. PMID: 30555393 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of trait and ability measures of emotional intelligence in medical students.Med Educ. 2009 Nov;43(11):1062-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2923.2009.03430.x. Med Educ. 2009. PMID: 19874499
-
The Three Models of Emotional Intelligence and Performance in a Hot and Cool go/no-go Task in Undergraduate Students.Front Behav Neurosci. 2017 Feb 22;11:33. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2017.00033. eCollection 2017. Front Behav Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28275343 Free PMC article.
-
Emotional intelligence evaluation tools used in allied health students: A scoping review.J Med Radiat Sci. 2025 Jun;72(2):177-192. doi: 10.1002/jmrs.851. Epub 2024 Dec 22. J Med Radiat Sci. 2025. PMID: 39711106 Free PMC article.
-
Measuring emotional intelligence with the Mayer-Salovery-Caruso Emotional Intelligence Test (MSCEIT).Psicothema. 2006;18 Suppl:34-41. Psicothema. 2006. PMID: 17295955 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Emotional Intelligence on Professional Performance and Stress Resilience Among Healthcare Practitioners.Cureus. 2024 Nov 20;16(11):e74113. doi: 10.7759/cureus.74113. eCollection 2024 Nov. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39712679 Free PMC article.
-
Methodological quality of 100 recent systematic reviews of health-related outcome measurement instruments: an overview of reviews.Qual Life Res. 2024 Oct;33(10):2593-2609. doi: 10.1007/s11136-024-03706-z. Epub 2024 Jul 3. Qual Life Res. 2024. PMID: 38961010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond emotional intelligence: The new construct of meta-emotional intelligence.Front Psychol. 2023 Apr 5;14:1096663. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1096663. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 37089723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Implementing a scoping review to explore sport officials' mental health.Front Sports Act Living. 2024 Jul 29;6:1436149. doi: 10.3389/fspor.2024.1436149. eCollection 2024. Front Sports Act Living. 2024. PMID: 39135607 Free PMC article.
-
Emotional Intelligence and Behavioural Addictions: A Systematic Review.J Clin Med. 2025 Feb 10;14(4):1125. doi: 10.3390/jcm14041125. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40004656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Salovey P., Mayer J.D. Emotional Intelligence. Imagin. Cogn. Personal. 1990;9:185–211. doi: 10.2190/DUGG-P24E-52WK-6CDG. - DOI
-
- Mayer J., Caruso D., Salovey P. Selecting a measure of emotional intelligence: The case for ability scales. In: Bar-On R., Parker J., editors. The handbook of Emotional Intelligence: Theory, Development, Assessment, and Application at Home, School, and in the Workplace. Jossey-Bass; New York, NY, USA: 2000. pp. 320–342.
-
- Mayer J., Salovey P. What is emotional intelligence? In: Salovey P., Sluyter D.J., editors. Emotional Development and Emotional Intelligence: Implications for Educators. Basic Books; New York, NY, USA: 1997. pp. 3–31.
-
- Petrides K.V., Furnham A. Trait emotional intelligence: Psychometric investigation with reference to established trait taxonomies. Eur. J. Pers. 2001;15:425–448. doi: 10.1002/per.416. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous