Applications of Cannabis Sativa L. in Food and Its Therapeutic Potential: From a Prohibited Drug to a Nutritional Supplement
- PMID: 34946779
- PMCID: PMC8708517
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26247699
Applications of Cannabis Sativa L. in Food and Its Therapeutic Potential: From a Prohibited Drug to a Nutritional Supplement
Abstract
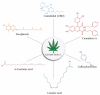
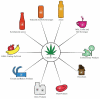
Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) is a herbaceous anemophilous plant that belongs to the Cannabinaceae family. The cannabis seed (hemp) has long been utilized as a food source and is commercially important as an edible oil source. In this review, the positive and negative health effects of cannabis, the relationship between cannabis and various diseases, and the use of cannabis in various food products have been discussed. In addition, the scientific literature on the potential use of cannabis and its derivatives as a dietary supplement for the prevention and treatment of inflammatory and chronic degenerative diseases in animals and humans has been reviewed. Cannabis is being developed as a key ingredient in a variety of food items, including bakery, confectionery, beverages, dairy, fruits, vegetables, and meat. Hemp seeds are high in readily digestible proteins, lipids, polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA), insoluble fiber, carbs, and favorable omega-6 PUFA acid to omega-3 PUFA ratio and have high nutritional value. The antioxidants of cannabis, such as polyphenols, help with anxiety, oxidative stress, and the risk of chronic illnesses, including cancer, neurological disorders, digestive problems, and skin diseases. Cannabis has been shown to have negative health impacts on the respiratory system, driving, and psychomotor functions, and the reproductive system. Overall, the purpose of this research is to stimulate more in-depth research on cannabis's adaptation in various foods and for the treatment of chronic illnesses.
Keywords: cannabidiol; cannabis; cannabis products; cannabis-infused foods; hemp; tetrahydrocannabinol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- De Petrocellis L., Ligresti A., Moriello A.S., Allarà M., Bisogno T., Petrosino S., Stott C.G., Di Marzo V. Effects of cannabinoids and cannabinoid-enriched Cannabis extracts on TRP channels and endocannabinoid metabolic enzymes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011;163:1479–1494. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.01166.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sirikantaramas S., Taura F., Tanaka Y., Ishikawa Y., Morimoto S., Shoyama Y. Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid synthase, the enzyme controlling marijuana psychoactivity, is secreted into the storage cavity of the glandular trichomes. Plant Cell Physiol. 2005;46:1578–1582. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pci166. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical