Marine Macroalgae, a Source of Natural Inhibitors of Fungal Phytopathogens
- PMID: 34946989
- PMCID: PMC8708330
- DOI: 10.3390/jof7121006
Marine Macroalgae, a Source of Natural Inhibitors of Fungal Phytopathogens
Abstract
Fungal phytopathogens are a growing problem all over the world; their propagation causes significant crop losses, affecting the quality of fruits and vegetables, diminishing the availability of food, leading to the loss of billions of euros every year. To control fungal diseases, the use of synthetic chemical fungicides is widely applied; these substances are, however, environmentally damaging. Marine algae, one of the richest marine sources of compounds possessing a wide range of bioactivities, present an eco-friendly alternative in the search for diverse compounds with industrial applications. The synthesis of such bioactive compounds has been recognized as part of microalgal responsiveness to stress conditions, resulting in the production of polyphenols, polysaccharides, lipophilic compounds, and terpenoids, including halogenated compounds, already described as antimicrobial agents. Furthermore, many studies, in vitro or in planta, have demonstrated the inhibitory activity of these compounds with respect to fungal phytopathogens. This review aims to gather the maximum of information addressing macroalgae extracts with potential inhibition against fungal phytopathogens, including the best inhibitory results, while presenting some already reported mechanisms of action.
Keywords: algae phenols; antifungal activity; bioactive compounds; brown algae; crop losses; fungal membrane disruption; fungal resistance; lipophilic compounds; macroalgae metabolites; plant pathogens.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
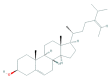
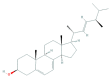

Similar articles
-
Seaweed as a Natural Source against Phytopathogenic Bacteria.Mar Drugs. 2022 Dec 28;21(1):23. doi: 10.3390/md21010023. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 36662196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
THE USE OF PLANTS TO PROTECT PLANTS AND FOOD AGAINST FUNGAL PATHOGENS: A REVIEW.Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2017 Jun 5;14(4):120-127. doi: 10.21010/ajtcam.v14i4.14. eCollection 2017. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28638874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Potential of Macroalgae for Sustainable Crop Production in Agriculture.Life (Basel). 2024 Oct 3;14(10):1263. doi: 10.3390/life14101263. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39459563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Networking-Based Metabolome and Bioactivity Analyses of Marine-Adapted Fungi Co-cultivated With Phytopathogens.Front Microbiol. 2018 Sep 6;9:2072. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02072. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30237790 Free PMC article.
-
Antifouling Compounds from Marine Macroalgae.Mar Drugs. 2017 Aug 28;15(9):265. doi: 10.3390/md15090265. Mar Drugs. 2017. PMID: 28846625 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Seaweed Extracts to Control Postharvest Phytopathogenic Fungi in Rocha Pear.J Fungi (Basel). 2023 Feb 17;9(2):269. doi: 10.3390/jof9020269. J Fungi (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36836383 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Activity of Arthrospira platensis as Antioxidant, Cytotoxic and Antifungal against Some Skin Diseases: Topical Cream Application.Mar Drugs. 2023 Feb 27;21(3):160. doi: 10.3390/md21030160. Mar Drugs. 2023. PMID: 36976209 Free PMC article.
-
Algae and Cyanobacteria Fatty Acids and Bioactive Metabolites: Natural Antifungal Alternative Against Fusarium sp.Microorganisms. 2025 Feb 17;13(2):439. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13020439. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40005804 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antihyperglycemic and anti-type 2 diabetic activity of marine hydroquinone isolated from brown algae (Dictyopteris polypodioides).J Tradit Complement Med. 2023 Mar 20;13(4):408-416. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2023.03.007. eCollection 2023 Jul. J Tradit Complement Med. 2023. PMID: 37396160 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Savary S., Ficke A., Aubertot J.-N., Hollier C. Crop Losses Due to Diseases and Their Implications for Global Food Production Losses and Food Security. Food Secur. 2012;4:519–537. doi: 10.1007/s12571-012-0200-5. - DOI
-
- Tleuova A.B., Wielogorska E., Talluri V.S.S.L.P., Štěpánek F., Elliott C.T., Grigoriev D.O. Recent Advances and Remaining Barriers to Producing Novel Formulations of Fungicides for Safe and Sustainable Agriculture. J. Control. Release. 2020;326:468–481. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.07.035. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kannan V.R., Bastas K.K., Devi R.S. Sustainable Approaches to Controlling Plant Pathogenic Bacteria. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2015. Scientific and Economic Impact of Plant Pathogenic Bacteria; pp. 369–392. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

