Ribosome Fate during Decoding of UGA-Sec Codons
- PMID: 34948001
- PMCID: PMC8704476
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms222413204
Ribosome Fate during Decoding of UGA-Sec Codons
Abstract
Decoding of genetic information into polypeptides occurs during translation, generally following the codon assignment rules of the organism's genetic code. However, recoding signals in certain mRNAs can overwrite the normal rules of translation. An exquisite example of this occurs during translation of selenoprotein mRNAs, wherein UGA codons are reassigned to encode for the 21st proteogenic amino acid, selenocysteine. In this review, we will examine what is known about the mechanisms of UGA recoding and discuss the fate of ribosomes that fail to incorporate selenocysteine.
Keywords: SECIS; SECIS-binding protein; nonsense-mediated decay; recoding; ribosome rescue; selenocysteine; selenoprotein; translation termination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
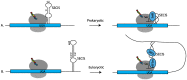
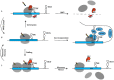
References
-
- Atkins J.F., Gesteland R.F. Nucleic Acids and Molecular Biology. Springer; New York, NY, USA: 2010. Recoding: Expansion of decoding rules enriches gene expression.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

