Development and Evaluation of Repurposed Etoricoxib Loaded Nanoemulsion for Improving Anticancer Activities against Lung Cancer Cells
- PMID: 34948081
- PMCID: PMC8705699
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms222413284
Development and Evaluation of Repurposed Etoricoxib Loaded Nanoemulsion for Improving Anticancer Activities against Lung Cancer Cells
Abstract
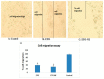
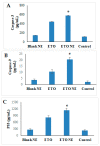
In the present work, novel modality for lung cancer intervention has been explored. Primary literature has established the potential role of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitor in regression of multiple forms of carcinomas. To overcome its poor water solubility and boost anticancer activity, etoricoxib (ETO) was chosen as a therapeutic candidate for repurposing and formulated into a nanoemulsion (NE). The prepared ETO loaded NE was characterized for the surface charge, droplet size, surface morphology, and in vitro release. The optimized ETO loaded NE was then investigated for its anticancer potential employing A549 lung cancer cell line via cytotoxicity, apoptotic activity, mitochondrial membrane potential activity, cell migration assay, cell cycle analysis, Caspase-3, 9, and p53 activity by ELISA and molecular biomarker analysis through RT-PCR test. The developed ETO-NE formulation showed adequate homogeneity in the droplet size distribution with polydispersity index (PDI) of (0.2 ± 0.03) and had the lowest possible droplet size (124 ± 2.91 nm) and optimal negative surface charge (-8.19 ± 1.51 mV) indicative of colloidal stability. The MTT assay results demonstrated that ETO-NE exhibited substantial anticancer activity compared to the free drug. The ETO-NE showed a substantially potent cytotoxic effect against lung cancer cells, as was evident from the commencement of apoptosis/necrotic cell death and S-phase cell cycle arrests in A549 cells. The study on these molecules through RT-PCR confirmed that ETO-NE is significantly efficacious in mitigating the abundance of IL-B, IL-6, TNF, COX-2, and NF-kB as compared to the free ETO and control group. The current study demonstrates that ETO-NE represents a feasible approach that could provide clinical benefits for lung cancer patients in the future.
Keywords: apoptosis; cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors; etoricoxib; inflammatory markers; lung cancer; nanoemulsion; repurposing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









Similar articles
-
In vitro and in vivo antitumor potential of carvacrol nanoemulsion against human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells via mitochondrial mediated apoptosis.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 9;8(1):144. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-18644-9. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29317755 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of nanoemulsion containing gemcitabine and evaluation of its cytotoxicity towards human fetal lung fibroblast (MRC5) and human lung carcinoma (A549) cells.Int J Nanomedicine. 2019 Sep 9;14:7323-7338. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S212635. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31686809 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation of Celery Essential Oil-Based Nanoemulsion by Ultrasonication and Evaluation of Its Potential Anticancer and Antibacterial Activity.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Oct 8;15:7651-7666. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S252640. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 33116493 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoemulsion enhances α-tocopherol succinate bioavailability in rats.Int J Pharm. 2016 Dec 30;515(1-2):506-514. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.10.026. Epub 2016 Oct 13. Int J Pharm. 2016. PMID: 27746330
-
Formulation Design, Statistical Optimization, and In Vitro Evaluation of a Naringenin Nanoemulsion to Enhance Apoptotic Activity in A549 Lung Cancer Cells.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020 Jul 15;13(7):152. doi: 10.3390/ph13070152. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32679917 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Nanoemulsion: An Emerging Novel Technology for Improving the Bioavailability of Drugs.Scientifica (Cairo). 2023 Oct 28;2023:6640103. doi: 10.1155/2023/6640103. eCollection 2023. Scientifica (Cairo). 2023. PMID: 37928749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preparation and Evaluation of Diosmin-Loaded Diphenylcarbonate-Cross-Linked Cyclodextrin Nanosponges for Breast Cancer Therapy.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Dec 23;16(1):19. doi: 10.3390/ph16010019. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36678517 Free PMC article.
-
Boosting the Anticancer Activity of Sunitinib Malate in Breast Cancer through Lipid Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticles Approach.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Jun 16;14(12):2459. doi: 10.3390/polym14122459. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35746034 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of TMEM106B exacerbates Tau pathology and neurodegeneration in PS19 mice.Acta Neuropathol. 2024 Mar 25;147(1):62. doi: 10.1007/s00401-024-02702-4. Acta Neuropathol. 2024. PMID: 38526799 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation and Evaluation of Chitosan Coated PLGA Nanoparticles Encapsulating Ivosidenib with Enhanced Cytotoxicity Against Human Liver Cancer Cells.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Apr 9;19:3461-3473. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S452989. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38617799 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Key Statistics for Lung Cancer. [(accessed on 25 July 2021)]. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/lung-cancer/about/key-statistics.html.
-
- Md S., Alhakamy N.A., Aldawsari H.M., Husain M., Kotta S., Abdullah S.T., Fahmy U.A., AlFaleh M.A., Asfour H.Z. Formulation Design, Statistical Optimization, and In Vitro Evaluation of a Naringenin Nanoemulsion to Enhance Apoptotic Activity in A549 Lung Cancer Cells. Pharmaceutics. 2020;13:152. doi: 10.3390/ph13070152. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Muralidharan R., Babu A., Amreddyn N., Basalingappa K., Mehta M., Chen A., Zhao Y.D., Kompella U.B., Munshi A., Ramesh R. Folate receptor-targeted nanoparticle delivery of HuR-RNAi suppresses lung cancer cell proliferation and migration. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2016;14:47. doi: 10.1186/s12951-016-0201-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

