Lupinus albus Protein Components Inhibit MMP-2 and MMP-9 Gelatinolytic Activity In Vitro and In Vivo
- PMID: 34948082
- PMCID: PMC8705115
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms222413286
Lupinus albus Protein Components Inhibit MMP-2 and MMP-9 Gelatinolytic Activity In Vitro and In Vivo
Abstract
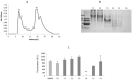
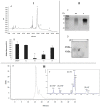
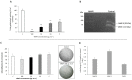
Matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 (MMP-2 and MMP-9) are regarded as important clinical targets due to their nodal-point role in inflammatory and oncological diseases. Here, we aimed at isolating and characterizing am MMP-2 and-9 inhibitor (MMPI) from Lupinus albus and at assessing its efficacy in vitro and in vivo. The protein was isolated using chromatographic and 2-D electrophoretic procedures and sequenced by using MALDI-TOF TOF and MS/MS analysis. In vitro MMP-2 and 9 inhibitions were determined on colon adenocarcinoma (HT29) cells, as well as by measuring the expression levels of genes related to these enzymes. Inhibitory activities were also confirmed in vivo using a model of experimental TNBS-induced colitis in mice, with oral administrations of 15 mg·kg-1. After chromatographic and electrophoretic isolation, the L. albus MMP-9 inhibitor was found to comprise a large fragment from δ-conglutin and, to a lower extent, small fragments of β-conglutin. In vitro studies showed that the MMPI successfully inhibited MMP-9 activity in a dose-dependent manner in colon cancer cells, with an IC50 of 10 µg·mL-1 without impairing gene expression nor cell growth. In vivo studies showed that the MMPI maintained its bioactivities when administered orally and significantly reduced colitis symptoms, along with a very significant inhibition of MMP-2 and -9 activities. Overall, results reveal a novel type of MMPI in lupine that is edible, proteinaceous in nature and soluble in water, and effective in vivo, suggesting a high potential application as a nutraceutical or a functional food in pathologies related to abnormally high MMP-9 activity in the digestive system.
Keywords: Lupinus albus protein; MMP inhibitor; MMP-2; MMP-9; gastrointestinal diseases; gelatinases; nutraceutical.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Berberine's effect on periodontal tissue degradation by matrix metalloproteinases: an in vitro and in vivo experiment.Phytomedicine. 2013 Oct 15;20(13):1203-10. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2013.06.001. Epub 2013 Jul 16. Phytomedicine. 2013. PMID: 23867651
-
Matrix metalloproteinase-9-mediated tissue injury overrides the protective effect of matrix metalloproteinase-2 during colitis.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009 Feb;296(2):G175-84. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.90454.2008. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19171847 Free PMC article.
-
An inhibitor from Lupinus bogotensis seeds effective against aspartic proteases from Hypothenemus hampei.Phytochemistry. 2010 Jun;71(8-9):923-9. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2010.03.006. Epub 2010 Mar 26. Phytochemistry. 2010. PMID: 20347105
-
Inhibitors of gelatinases (MMP-2 and MMP-9) for the management of hematological malignancies.Eur J Med Chem. 2021 Nov 5;223:113623. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113623. Epub 2021 Jun 12. Eur J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34157437 Review.
-
Role of MMP-2 and MMP-9 and their natural inhibitors in liver fibrosis, chronic pancreatitis and non-specific inflammatory bowel diseases.Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2014 Dec;13(6):570-9. doi: 10.1016/s1499-3872(14)60261-7. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2014. PMID: 25475858 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Potential of Deflamin against Colorectal Cancer Development and Progression.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Dec 14;14(24):6182. doi: 10.3390/cancers14246182. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36551666 Free PMC article.
-
Lupin Protein Concentrate as a Novel Functional Food Additive That Can Reduce Colitis-Induced Inflammation and Oxidative Stress.Nutrients. 2022 May 18;14(10):2102. doi: 10.3390/nu14102102. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35631241 Free PMC article.
-
Deflamin Attenuated Lung Tissue Damage in an Ozone-Induced COPD Murine Model by Regulating MMP-9 Catalytic Activity.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 7;25(10):5063. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105063. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791100 Free PMC article.
-
New Alternatives to Milk From Pulses: Chickpea and Lupin Beverages With Improved Digestibility and Potential Bioactivities for Human Health.Front Nutr. 2022 Jul 14;9:852907. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.852907. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35911116 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gonçalves R.F.S., Martins J.T., Duarte C.M.M., Vicente A.A., Pinheiro A.C. Advances in nutraceutical delivery systems: From formulation design for bioavailability enhancement to efficacy and safety evaluation. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018;78:270–291. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2018.06.011. - DOI
-
- Lee I.K., Vansaun M.N., Shim J.H., Matrisian L.M., Gorden D.L. Increased metastases are associated with inflammation and matrix metalloproteinase-9 activity at incision sites in a murine model of peritoneal dissemination of colorectal cancer. J. Surg. Res. 2013;180:252–259. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2012.04.074. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

