Characterizing the Interaction between the HTLV-1 Transactivator Tax-1 with Transcription Elongation Factor ELL2 and Its Impact on Viral Transactivation
- PMID: 34948391
- PMCID: PMC8705299
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms222413597
Characterizing the Interaction between the HTLV-1 Transactivator Tax-1 with Transcription Elongation Factor ELL2 and Its Impact on Viral Transactivation
Abstract
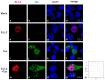
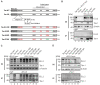
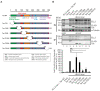
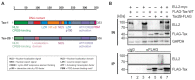
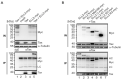
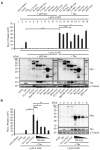
The human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1)-encoded transactivator and oncoprotein Tax-1 is essential for HTLV-1 replication. We recently found that Tax-1 interacts with transcription elongation factor for RNA polymerase II 2, ELL2, which enhances Tax-1-mediated transactivation of the HTLV-1 promotor. Here, we characterize the Tax-1:ELL2 interaction and its impact on viral transactivation by confocal imaging, co-immunoprecipitation, and luciferase assays. We found that Tax-1 and ELL2 not only co-precipitate, but also co-localize in dot-like structures in the nucleus. Tax-1:ELL2 complex formation occurred independently of Tax-1 point mutations, which are crucial for post translational modifications (PTMs) of Tax-1, suggesting that these PTMs are irrelevant for Tax-1:ELL2 interaction. In contrast, Tax-1 deletion mutants lacking either N-terminal (aa 1-37) or C-terminal regions (aa 150-353) of Tax-1 were impaired in interacting with ELL2. Contrary to Tax-1, the related, non-oncogenic Tax-2B from HTLV-2B did not interact with ELL2. Finally, we found that ELL2-R1 (aa 1-353), which carries an RNA polymerase II binding domain, and ELL2-R3 (aa 515-640) are sufficient to interact with Tax-1; however, only ELL2-truncations expressing R1 could enhance Tax-1-mediated transactivation of the HTLV-1 promoter. Together, this study identifies domains in Tax-1 and ELL2 being required for Tax-1:ELL2 complex formation and for viral transactivation.
Keywords: ELL2; HTLV-1; Tax-1; Tax-2; human T-cell leukemia virus type 1; transcription elongation factor for RNA polymerase II; viral oncoprotein; viral transactivation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



References
-
- Poiesz B.J., Ruscetti F.W., Gazdar A.F., Bunn P.A., Minna J.D., Gallo R.C. Detection and isolation of type C retrovirus particles from fresh and cultured lymphocytes of a patient with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1980;77:7415–7419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7415. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- GRK2504, project number 401821119, subprojects A2 (to A.K.T.K.) and C2 (to H.S.)/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft
- TH2166/1-1/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft
- Milk-TV, 01Kl2023/Federal Ministry of Education and Research
- A91/Interdisciplinary Center for Clinical Research (IZKF) at the Medical Faculty of FAU Erlangen-Nürnberg
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

