Luteolin Improves Perivascular Adipose Tissue Profile and Vascular Dysfunction in Goto-Kakizaki Rats
- PMID: 34948468
- PMCID: PMC8706309
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms222413671
Luteolin Improves Perivascular Adipose Tissue Profile and Vascular Dysfunction in Goto-Kakizaki Rats
Abstract
We investigated the effects of luteolin on metabolism, vascular reactivity, and perivascular adipose tissue (PVAT) in nonobese type 2 diabetes mellitus animal model, Goto-Kakizaki (GK) rats.
Methods: Wistar and GK rats were divided in two groups: (1) control groups treated with vehicle; (2) groups treated with luteolin (10 mg/kg/day, for 2 months). Several metabolic parameters such as adiposity index, lipid profile, fasting glucose levels, glucose and insulin tolerance tests were determined. Endothelial function and contraction studies were performed in aortas with (PVAT+) or without (PVAT-) periaortic adipose tissue. We also studied vascular oxidative stress, glycation and assessed CRP, CCL2, and nitrotyrosine levels in PVAT.
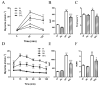
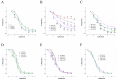
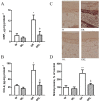
Results: Endothelial function was impaired in diabetic GK rats (47% (GK - PVAT) and 65% (GK + PVAT) inhibition of maximal endothelial dependent relaxation) and significantly improved by luteolin treatment (29% (GK - PVAT) and 22% (GK + PVAT) inhibition of maximal endothelial dependent relaxation, p < 0.01). Vascular oxidative stress and advanced glycation end-products' levels were increased in aortic rings (~2-fold, p < 0.05) of diabetic rats and significantly improved by luteolin treatment (to levels not significantly different from controls). Periaortic adipose tissue anti-contractile action was significantly rescued with luteolin administration (p < 0.001). In addition, luteolin treatment significantly recovered proinflammatory and pro-oxidant PVAT phenotype, and improved systemic and metabolic parameters in GK rats.
Conclusions: Luteolin ameliorates endothelial dysfunction in type 2 diabetes and exhibits therapeutic potential for the treatment of vascular complications associated with type 2 diabetes.
Keywords: endothelial dysfunction; inflammation; luteolin; oxidative stress; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Okada S., Hiuge A., Makino H., Nagumo A., Takaki H., Konishi H., Goto Y., Yoshimasa Y., Miyamoto Y. Effect of exercise intervention on endothelial function and incidence of cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2010;17:828–833. doi: 10.5551/jat.3798. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

