Alexithymia, Dissociation, and Family Functioning in a Sample of Online Gamblers: A Moderated Mediation Study
- PMID: 34948900
- PMCID: PMC8707594
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph182413291
Alexithymia, Dissociation, and Family Functioning in a Sample of Online Gamblers: A Moderated Mediation Study
Abstract
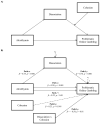
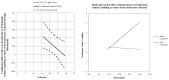
The diffusion of the internet and technological progress have made gambling on online platforms possible, also making it more anonymous, convenient, and available, increasing the risk of pathological outcomes for vulnerable individuals. Given this context, the present study explores the role of some protective and risk factors for problematic gambling in online gamblers by focusing on the interaction between alexithymia, dissociation, and family functioning. A sample of 193 online gamblers (Mage = 28.8 years, SD = 10.59; 17% females, 83% males) completed the South Oaks Gambling Screen, Twenty-Items Toronto Alexithymia Scale, Dissociative Experience Scale-II, and Family Adaptability and Cohesion Evaluation Scales-IV through an online survey. MANOVA, ANOVA and moderated mediation analyses were carried out to analyse the data. Significant differences in cohesive family functioning, alexithymia and dissociation have been found between online gamblers with problematic, at-risk or absent levels of gambling disease. Furthermore, the results showed a significant and positive association between alexithymia and problematic online gambling, partially mediated by dissociation, with the moderation of cohesive family functioning. Such data may have relevant clinical implications, highlighting the interaction of some core personal and environmental variables that may be involved in the etiology of online pathological gambling and could be kept in mind to tailor preventive interventions.
Keywords: internet gambling; moderated mediation analysis; online gambling; pathological gambling; protective factors; risk factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Problematic Gambling Behavior in a Sample of Gamblers: The Role of Alexithymia, Dissociation Features, and External Locus of Control.J Gambl Stud. 2024 Dec;40(4):2077-2091. doi: 10.1007/s10899-024-10322-6. Epub 2024 Jun 4. J Gambl Stud. 2024. PMID: 38831237 Free PMC article.
-
Alexithymia and gambling: a risk factor for all gamblers?J Gambl Stud. 2013 Mar;29(1):83-96. doi: 10.1007/s10899-012-9297-x. J Gambl Stud. 2013. PMID: 22367561
-
[Psychopathology in online pathological gamblers: a preliminary study].Encephale. 2012 Apr;38(2):156-63. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2011.01.009. Epub 2011 Mar 24. Encephale. 2012. PMID: 22516274 French.
-
Online Gambling: A Systematic Review of Risk and Protective Factors in the Adult Population.J Gambl Stud. 2024 Jun;40(2):673-699. doi: 10.1007/s10899-023-10258-3. Epub 2023 Nov 14. J Gambl Stud. 2024. PMID: 37964161 Free PMC article.
-
[Internet gambling: what are the risks?].Encephale. 2012 Feb;38(1):42-9. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2011.01.014. Epub 2011 Apr 8. Encephale. 2012. PMID: 22381723 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Problematic Gambling Behavior in a Sample of Gamblers: The Role of Alexithymia, Dissociation Features, and External Locus of Control.J Gambl Stud. 2024 Dec;40(4):2077-2091. doi: 10.1007/s10899-024-10322-6. Epub 2024 Jun 4. J Gambl Stud. 2024. PMID: 38831237 Free PMC article.
-
Family Functioning Styles and Exercise Addiction: Disengaged, Enmeshed, and Rigid Family Patterns Are Associated with Exercise Addiction.Eur J Investig Health Psychol Educ. 2024 Jan 3;14(1):148-163. doi: 10.3390/ejihpe14010010. Eur J Investig Health Psychol Educ. 2024. PMID: 38248130 Free PMC article.
-
Mediating Effect of Emotional Symptoms on the Association Between Alexithymia and Substance Dependence in Patients with Substance Use Disorder: The Protective Role of Family Support and Self-Efficacy.Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2024 Nov 8;17:3863-3874. doi: 10.2147/PRBM.S478305. eCollection 2024. Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2024. PMID: 39534555 Free PMC article.
-
The Interplay Between Problematic Online Pornography Use, Psychological Stress, Emotion Dysregulation and Insomnia Symptoms During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Mediation Analysis.Nat Sci Sleep. 2022 Jan 20;14:83-92. doi: 10.2147/NSS.S348242. eCollection 2022. Nat Sci Sleep. 2022. PMID: 35082545 Free PMC article.
-
The Mediating Role of Affect Dysregulation and Dissociation in the Relationship Between Attachment and Compulsive Online Shopping: A Path Analysis Model.Clin Neuropsychiatry. 2024 Jun;21(3):217-224. doi: 10.36131/cnfioritieditore20240307. Clin Neuropsychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38988680 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Publishing; Washington, DC, USA: 2013.
-
- McCormack A., Griffiths M.D. Motivating and inhibiting factors in online gambling behaviour: A grounded theory study. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2012;10:39–53. doi: 10.1007/s11469-010-9300-7. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical