Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: a meta-analysis of 8 mm versus 10 mm stents
- PMID: 34950255
- PMCID: PMC8669991
- DOI: 10.5114/wiitm.2021.104198
Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: a meta-analysis of 8 mm versus 10 mm stents
Abstract
Introduction: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) is an approach that is used to alleviate portal hypertension-related symptoms. The optimal stent diameter for TIPS remains controversial.
Aim: To assess outcomes in patients who underwent TIPS using 8 mm and 10 mm stents.
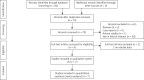
Material and methods: The PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library databases were queried for all pertinent studies. The meta-analysis was conducted using RevMan v5.3. This meta-analysis was registered at the PROSPERO website (Number: CRD42020212392).
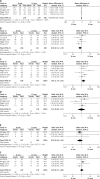
Results: Eighty-two potentially relevant articles were initially detected, with seven of these ultimately being included in this meta-analysis. Patients in the 10 mm stent group exhibited a significantly higher Δportosystemic pressure gradient (ΔPPG) relative to the 8 mm group (p = 0.04), whereas no differences between groups were observed with respect to postoperative hepatic encephalopathy (HE, p = 0.25), re-bleeding (p = 0.82), liver transplantation (p = 0.45), or mortality (p = 0.43) rates. The TIPS dysfunction rate was significant lower in the 10 mm group (p = 0.01). In Asian studies, the postoperative HE rate was found to be significantly lower in the 8 mm group relative to the 10 mm group (p = 0.02), whereas all other endpoints were comparable between these groups. In Western studies, ΔPPG values were significantly greater in the 10 mm group (p < 0.0001), whereas all other endpoint data were comparable between these groups.
Conclusions: TIPS with 10 mm stents provides a lower TIPS dysfunction rate. However, 8 mm stents may be recommended for Asian patients, as they can decrease the risk of postoperative HE.
Keywords: 10 mm; 8 mm; meta-analysis; transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt.
Copyright: © 2021 Fundacja Videochirurgii.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Song T, Rössle M, He F, et al. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for hepatorenal syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Dig Liver Dis. 2018;50:323–30. - PubMed
-
- Tsauo J, Zhao H, Zhang X, et al. Effect of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt creation on pulmonary gas exchange in patients with hepatopulmonary syndrome: a prospective study. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2019;30:170–7. - PubMed
-
- Lv Y, Qi X, He C, et al. Covered TIPS versus endoscopic band ligation plus propranolol for the prevention of variceal rebleeding in cirrhotic patients with portal vein thrombosis: a randomised controlled trial. Gut. 2018;67:2156–68. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources