Computed tomography-guided localization for multiple pulmonary nodules: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 34950257
- PMCID: PMC8669986
- DOI: 10.5114/wiitm.2021.104199
Computed tomography-guided localization for multiple pulmonary nodules: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Preoperative computed tomography (CT)-guided localization is commonly employed to facilitate video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS)-guided diagnostic wedge resection of pulmonary nodules (PNs).
Aim: The present meta-analysis was conducted with the goal of better evaluating the feasibility, safety, and clinical efficacy of preoperative CT-guided localization for multiple PNs (MPNs).
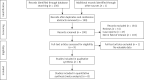
Material and methods: PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Library databases were reviewed in order to identify all relevant studies published as of June 2020. Random effects modeling was then used to evaluate the pooled data. The meta-analysis was conducted using Stata v12.0 software.
Results: Eight relevant studies were identified for inclusion in the present meta-analysis. In total, 345 patients with 799 PNs were treated with preoperative CT-guided localization and subsequent wedge resection. The overall pooled technical success rate based on the nodules and patients was calculated to be 97% (95% confidence interval (CI): 0.94-0.99) and 92% (95% CI: 0.86-0.97), respectively. The overall pooled incidence rate of complications was calculated to be 40% (95% CI: 0.16-0.63). Significant heterogeneity was observed among the studies for all the parameters described above (I2 = 74.5%, 77.7%, and 96.3%, respectively). No significant differences were detected in the technical success of localization and incidence of complications between coil and hook-wire groups. The risk of publication bias in the reporting of technical success rate of localization based on both nodules and patients was found to be high (p < 0.001 and < 0.001, respectively).
Conclusions: Preoperative CT-guided localization may be effective in guiding VATS-guided wedge resection in patients with MPNs.
Keywords: computed tomography; localization; lung nodule; multiple.
Copyright: © 2021 Fundacja Videochirurgii.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Fu YF, Zhang M, Wu WB, et al. Coil localization-guided video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery for lung nodules. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2018;28:292–7. - PubMed
-
- Gruber-Rouh T, Naguib NNN, Beeres M, et al. CT-guided hook-wire localisation prior to video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery of pulmonary lesions. Clin Radiol. 2017;72:898.e7–8.e11. - PubMed
-
- Zhang ZD, Wang HL, Liu XY, et al. Methylene blue versus coil-based computed tomography-guided localization of lung nodules. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2020;68:540–4. - PubMed
-
- Finley RJ, Mayo JR, Grant K, et al. Preoperative computed tomography-guided microcoil localization of small peripheral pulmonary nodules: a prospective randomized controlled trial. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2015;149:26–31. - PubMed
-
- Iguchi T, Hiraki T, Gobara H, et al. Transfissural route used for preoperative localization of small pulmonary lesions with a short hook wire and suture system. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2015;38:222–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources