Recent progress in treatments of rheumatoid arthritis: an overview of developments in biologics and small molecules, and remaining unmet needs
- PMID: 34951925
- PMCID: PMC8709568
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab609
Recent progress in treatments of rheumatoid arthritis: an overview of developments in biologics and small molecules, and remaining unmet needs
Abstract
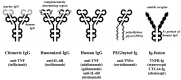
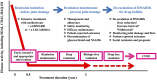
Through treatment with biological DMARDs (bDMARDs) or targeted synthetic (tsDMARDs) such as Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors in addition to MTX, clinical remission has become a realistic therapeutic goal for the majority of patients with RA, and sustained remission facilitates prevention of joint damage and physical dysfunction. Long-term safety and sustained inhibition of structural changes and physical dysfunction by bDMARDs have been reported. The development of next-generation bDMARDs and expansion of their indications to various autoimmune diseases are expected. Five JAK inhibitors show comparable efficacy to bDMARDs, and the latest ones are effective for overcoming difficult-to-treat RA regardless of prior medications. Patients treated with JAK inhibitors should be adequately screened and monitored for infection, cardiovascular disorders, thrombosis, malignancies and so on. Advances in therapeutic strategies, including the differential use of therapeutic drugs and de-escalation of treatment after remission induction, are prioritized.
Keywords: rheumatoid arthritis; DMARD; bDMARD; clinical trial; csDMARD; remission; safety; treatment; tsDMARD.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology.
Figures
References
-
- Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Barton A. et al. Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2018;4:18001. - PubMed
-
- Smolen JS, Landewé RBM, Bijlsma JWJ. et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2019 update. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79:685–99. - PubMed
-
- Weinblatt ME, Bathon JM, Kremer JM. et al. Safety and efficacy of etanercept beyond 10 years of therapy in North American patients with early and longstanding rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2011;63:373–82. - PubMed
-
- Keystone EC, Breedveld FC, van der Heijde D. et al. Longterm effect of delaying combination therapy with tumor necrosis factor inhibitor in patients with aggressive early rheumatoid arthritis: 10-year efficacy and safety of adalimumab from the randomized controlled PREMIER trial with open-label extension. J Rheumatol 2014;41:5–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

