Final efficacy analysis, interim safety analysis, and immunogenicity of a single dose of recombinant novel coronavirus vaccine (adenovirus type 5 vector) in adults 18 years and older: an international, multicentre, randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial
- PMID: 34953526
- PMCID: PMC8700283
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02753-7
Final efficacy analysis, interim safety analysis, and immunogenicity of a single dose of recombinant novel coronavirus vaccine (adenovirus type 5 vector) in adults 18 years and older: an international, multicentre, randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial
Erratum in
-
Department of Error.Lancet. 2022 Jan 15;399(10321):236. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00019-8. Lancet. 2022. PMID: 35033218 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: The Ad5-nCoV vaccine is a single-dose adenovirus type 5 (Ad5) vectored vaccine expressing the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein that was well-tolerated and immunogenic in phase 1 and 2 studies. In this study, we report results on the final efficacy and interim safety analyses of the phase 3 trial.
Methods: This double-blind, randomised, international, placebo-controlled, endpoint-case driven, phase 3, clinical trial enrolled adults aged 18 years older at study centres in Argentina, Chile, Mexico, Pakistan, and Russia. Participants were eligible for the study if they had no unstable or severe underlying medical or psychiatric conditions; had no history of a laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection; were not pregnant or breastfeeding; and had no previous receipt of an adenovirus-vectored, coronavirus, or SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. After informed consent was obtained, 25 mL of whole blood was withdrawn from all eligible participants who were randomised in a 1:1 ratio to receive a single intramuscular dose of 0·5 mL placebo or a 0·5 mL dose of 5 × 1010 viral particle (vp)/mL Ad5-nCoV vaccine; study staff and participants were blinded to treatment allocation. All participants were contacted weekly by email, telephone, or text message to self-report any symptoms of COVID-19 illness, and laboratory testing for SARS-CoV-2 was done for all participants with any symptoms. The primary efficacy objective evaluated Ad5-nCoV in preventing symptomatic, PCR-confirmed COVID-19 infection occurring at least 28 days after vaccination in all participants who were at least 28 days postvaccination on Jan 15, 2021. The primary safety objective evaluated the incidence of any serious adverse events or medically attended adverse events postvaccination in all participants who received a study injection. This trial is closed for enrolment and is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04526990).
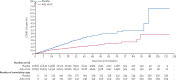
Findings: Study enrolment began on Sept 22, 2020, in Pakistan, Nov 6, 2020, in Mexico, Dec 2, 2020, in Russia and Chile, and Dec 17, 2020, in Argentina; 150 endpoint cases were reached on Jan 15, 2021, triggering the final primary efficacy analysis. One dose of Ad5-nCoV showed a 57·5% (95% CI 39·7-70·0, p=0·0026) efficacy against symptomatic, PCR-confirmed, COVID-19 infection at 28 days or more postvaccination (21 250 participants; 45 days median duration of follow-up [IQR 36-58]). In the primary safety analysis undertaken at the time of the efficacy analysis (36 717 participants), there was no significant difference in the incidence of serious adverse events (14 [0·1%] of 18 363 Ad5-nCoV recipients and 10 [0·1%] of 18 354 placebo recipients, p=0·54) or medically attended adverse events (442 [2·4%] of 18 363 Ad5-nCoV recipients and 411 [2·2%] of 18 354 placebo recipients, p=0·30) between the Ad5-nCoV or placebo groups, or any serious adverse events considered related to the study product (none in both Ad5-nCoV and placebo recipients). In the extended safety cohort, 1004 (63·5%) of 1582 of Ad5-nCoV recipients and 729 (46·4%) of 1572 placebo recipients reported a solicited systemic adverse event (p<0·0001), of which headache was the most common (699 [44%] of Ad5-nCoV recipients and 481 [30·6%] of placebo recipients; p<0·0001). 971 (61·3%) of 1584 Ad5-nCoV recipients and 314 (20·0%) of 1573 placebo recipients reported an injection-site adverse event (p<0·0001), of which pain at the injection site was the most frequent; reported by 939 (59%) Ad5-nCoV recipients and 303 (19%) placebo recipients.
Interpretation: One dose of Ad5-nCoV is efficacious and safe in healthy adults aged 18 years and older.
Funding: CanSino Biologics and the Beijing Institute of Biotechnology.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests JG and TZ are employees of and own stock in CanSino Biologics, and LB is a senior scientific advisor to CanSino Biologics. All other authors received funding to their institutions to perform the clinical trial but did not receive any personal funding.
Figures

Comment in
-
Efficacy of an adenovirus type 5 vectored SARS-CoV-2 vaccine.Lancet. 2022 Jan 15;399(10321):212-213. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02834-8. Epub 2021 Dec 23. Lancet. 2022. PMID: 34953524 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Johns Hopkins University COVID-19 dashboard by the Centre for Systems Science and Engineering. 2021. https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html/
-
- WHO COVID-19 vaccines. 2021. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/covid-19...
-
- WHO COVID-19 vaccine tracker and landscape. 2021. https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/draft-landscape-of-covid-19-cand...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

