PEDOT-AuNPs-based impedimetric immunosensor for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies
- PMID: 34955549
- PMCID: PMC8684030
- DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2021.139757
PEDOT-AuNPs-based impedimetric immunosensor for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies
Abstract
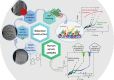
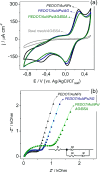
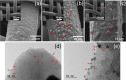
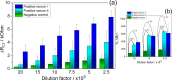
Electrochemical sensors and biosensors are useful techniques for fast, inexpensive, sensitive, and easy detection of innumerous specimen. In face of COVID-19 pandemic, it became evident the necessity of a rapid and accurate diagnostic test, so the impedimetric immunosensor approach can be a good alternative to replace the conventional tests due to the specific antibody-antigen binding interaction and the fast response in comparison to traditional methods. In this work, a modified electrode with electrosynthesized PEDOT and gold nanoparticles followed by the immobilization of truncated nucleoprotein (N aa160-406aa) was used for a fast and reliable detection of antibodies against COVID-19 in human serum sample. The method consists in analyzing the charge-transfer resistance (RCT) variation before and after the modified electrode comes into contact with the positive and negative serum sample for COVID-19, using [Fe(CN)6]3-/4- as a probe. The results show a linear and selective response for serum samples diluted in a range of 2.5 × 103 to 20 × 103. Also, the electrode material was fully characterized by Raman spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy and scanning electron microscopy coupled with EDS, indicating that the gold nanoparticles were well distributed around the polymer matrix and the presence of the biological sample was confirmed by EDS analysis. EIS measurements allowed to differentiate the negative and positive samples by the difference in the RCT magnitude, proving that the material developed here has potential properties to be applied in impedimetric immunosensors for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in about 30 min.
Keywords: COVID-19; Gold nanoparticles; Impedance spectroscopy; Impedimetric biosensor; PEDOT; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
none. The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Orooji Y., Sohrabi H., Hemmat N., Oroojalian F., Baradaran B., Mokhtarzadeh A., Mohaghegh M., Karimi-Maleh H. An overview on SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) and other human coronaviruses and their detection capability via amplification assay. Chem. Sens., Biosens., Immunosens. Clin. Assays, Nano-Micro Lett. 2020;13:18. - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization, “Coronavirus disease (COVID-19), https://www.who.int/health-topics/coronavirus#tab=tab_1. September 2021.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
