Maresin 1 Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Kidney Injury via Inhibiting NOX4/ROS/NF-κB Pathway
- PMID: 34955852
- PMCID: PMC8703041
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.782660
Maresin 1 Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Kidney Injury via Inhibiting NOX4/ROS/NF-κB Pathway
Abstract
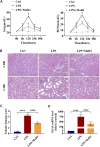
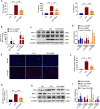
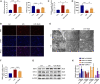
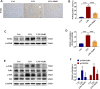
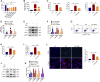
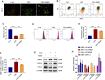
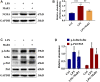
Sepsis-associated acute kidney injury (S-AKI) is a common complication in hospitalized and critically ill patients, which increases the risk of multiple comorbidities and is associated with extremely high mortality. Maresin 1 (MaR1), a lipid mediator derived from the omega-3 fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid has been reported to protect against inflammation and promote the regression of acute inflammation. This study proposed to systematically investigate the renoprotective effects and potential molecular mechanism of MaR1 in septic acute kidney injury. We established a S-AKI animal model by a single intraperitoneal injection of lipopolysaccharide (LPS), 10 mg/kg, on male C57BL/6J mice. LPS-stimulated (100 μg/ml) mouse kidney tubular epithelium cells (TCMK-1) were used to simulate septic AKI in vitro. The results showed that pretreatment with MaR1 significantly reduced serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen levels as well as tubular damage scores and injury marker neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in septic AKI mice. Meanwhile, MaR1 administration obviously diminished pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and MCP-1), downregulated BAX and cleaved caspase-3 expression, and upregulated BCL-2 expression in the injured kidney tissues and TCMK-1 cells. In addition, MaR1 reduced malondialdehyde production and improved the superoxide dismutase activity of renal tissues while inhibiting reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and protecting the mitochondria. Mechanistically, LPS stimulated the expression of the NOX4/ROS/NF-κB p65 signaling pathway in S-AKI kidneys, while MaR1 effectively suppressed the activation of the corresponding pathway. In conclusion, MaR1 attenuated kidney inflammation, apoptosis, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial dysfunction to protect against LPS-induced septic AKI via inhibiting the NOX4/ROS/NF-κB p65 signaling pathway.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; apoptosis; inflammation; lipopolysaccharide; maresin 1; mitochondrial dysfunction.
Copyright © 2021 Li, Zhang, Wang, Jiang, Qin, Zhao and Su.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Intersection of Acute Kidney Injury and Non-Coding RNAs: Inflammation.Front Physiol. 2022 Jun 9;13:923239. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.923239. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35755446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flavonoid fisetin alleviates kidney inflammation and apoptosis via inhibiting Src-mediated NF-κB p65 and MAPK signaling pathways in septic AKI mice.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Feb;122:109772. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109772. Epub 2019 Dec 30. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 31918290
-
NOX4 is a potential therapeutic target in septic acute kidney injury by inhibiting mitochondrial dysfunction and inflammation.Theranostics. 2023 May 8;13(9):2863-2878. doi: 10.7150/thno.81240. eCollection 2023. Theranostics. 2023. PMID: 37284448 Free PMC article.
-
Maresin 1 Mitigates Sepsis-Associated Acute Kidney Injury in Mice via Inhibition of the NF-κB/STAT3/MAPK Pathways.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Nov 7;10:1323. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01323. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31787899 Free PMC article.
-
Role of curcumin in the treatment of acute kidney injury: research challenges and opportunities.Phytomedicine. 2022 Sep;104:154306. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154306. Epub 2022 Jul 3. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 35809376 Review.
Cited by
-
The Intersection of Acute Kidney Injury and Non-Coding RNAs: Inflammation.Front Physiol. 2022 Jun 9;13:923239. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.923239. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35755446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New insights into Sirt1: potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of cerebral ischemic stroke.Front Cell Neurosci. 2023 Aug 9;17:1228761. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1228761. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37622049 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protection of Ndrg2 deficiency on renal ischemia-reperfusion injury via activating PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy.Chin Med J (Engl). 2024 Nov 5;137(21):2603-2614. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002957. Epub 2024 Feb 26. Chin Med J (Engl). 2024. PMID: 38407220 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Inflammatory Imbalance in Chronic Kidney Disease: Focus on Anti-Inflammatory and Resolution Mediators.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 27;26(7):3072. doi: 10.3390/ijms26073072. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40243751 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methotrexate-Induced Alteration of Renal Aquaporins 1 and 2, Oxidative Stress and Tubular Apoptosis Can Be Attenuated by Omega-3 Fatty Acids Supplementation.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 24;23(21):12794. doi: 10.3390/ijms232112794. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36361584 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

