Effects of bilateral early breast sucking and unilateral early breast sucking within 2 h after delivery on lactation, breast distending pain and postpartum lochia
- PMID: 34956517
- PMCID: PMC8661153
Effects of bilateral early breast sucking and unilateral early breast sucking within 2 h after delivery on lactation, breast distending pain and postpartum lochia
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effects of bilateral early breast sucking and unilateral early breast sucking within 2 h after delivery on lactation, breast distending pain and postpartum lochia.
Methods: The clinical data of 128 parturients were analyzed retrospectively. According to the different ways of early breast suction, the parturients were divided into control group (n=64) and observation group (n=64). Among them, unilateral early sucking was performed within 2 h after delivery in the control group, while bilateral early sucking was carried out in the observation group. We compared the lactation, breast distending pain, postpartum lochia, nutritional status, coagulation index, complications and breast feeding success rate.
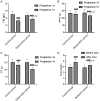
Results: The lactation amount of the observation group was higher than that of the control group on the 3rd, 5th and 7th day after delivery; the VAS scores showed opposite trends; the amount of lochia in the observation group was less than that in the control group; the ALb, PA and Hb levels in the observation group were higher on the 7th day after delivery. Compared with the control group, the FIB, PT and APTT time was shorter and the D-D level was higher; the incidence of postpartum hemorrhage, galactostasis and postpartum depression in the observation group was lower, and the success rate of feeding on the 1st, 3rd and 7th day after delivery was higher in the observation group seven days after intervention.
Conclusion: Bilateral early breast sucking within 2 h after delivery is helpful to increase lactation and reduce breast distending pain and postpartum lochia. It also promotes maternal nutritional status and coagulation function, reduces the incidence of postpartum complications, and improves the breastfeeding rate.
Keywords: 2 h after delivery; bilateral early breast sucking; breast distending pain; maternal lactation; postpartum lochia; unilateral early sucking.
AJTR Copyright © 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Samii SS, Rico JE, Mathews AT, Davis AN, Orndorff CL, Aromeh LO, McFadden JW. Effects of body condition score on direct and indirect measurements of insulin sensitivity in periparturient dairy cows. Animal. 2019;13:2547–2555. - PubMed
-
- Karis P, Jaakson H, Ling K, Bruckmaier RM, Gross JJ, Pärn P, Kaart T, Ots M. Body condition and insulin resistance interactions with periparturient gene expression in adipose tissue and lipid metabolism in dairy cows. J Dairy Sci. 2020;103:3708–3718. - PubMed
-
- Kenéz Á, Ruda L, Dänicke S, Huber K. Insulin signaling and insulin response in subcutaneous and retroperitoneal adipose tissue in Holstein cows during the periparturient period. J Dairy Sci. 2019;102:11718–11729. - PubMed
-
- Hyde ML, Wilkens MR, Fraser DR. In vivo measurement of strontium absorption from the rumen of dairy cows as an index of calcium absorption capacity. J Dairy Sci. 2019;102:5699–5705. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous