CD146 as a Prognostic-Related Biomarker in ccRCC Correlating With Immune Infiltrates
- PMID: 34956870
- PMCID: PMC8692769
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.744107
CD146 as a Prognostic-Related Biomarker in ccRCC Correlating With Immune Infiltrates
Abstract
Backgrounds: CD146 is highly expressed in various malignant tumors and associated with the poor prognosis. However, the role of CD146 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) is still unknown. This study aimed to identify the role of CD146 in ccRCC by integrated bioinformatics analysis.
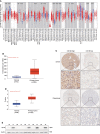
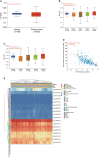
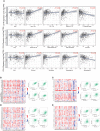
Methods: CD146 mRNA expression and methylation data in ccRCC was examined using the TIMER, UALCAN, and MethSurv databases. CD146 expression in paraffin-embedded tissues (140 cancer samples and 140 paracancer tissues) from our cohort were examined by immunohistochemistry assay. The LinkedOmics database was used to study the signaling pathways related to CD146 expression. TIMER and TISIDB were used to analyze the correlations among CD146, CD146-coexpressed genes, tumor-infiltrating immune cells, and immunomodulators. The relationship between CD146 and drug response in renal cancer cell lines was analyzed by the CTRP and CCLE databases.
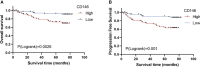
Results: The mRNA and protein levels of CD146 were elevated in ccRCC tissues than that in paracancer tissues. The DNA methylation of CD146 in ccRCC tissues were lower than that in normal tissues. Importantly, high CD146 expression was associated with poor prognosis in patients with ccRCC. Furthermore, multivariate Cox regression analysis showed that CD146 was an independent prognostic factor in ccRCC. GO and KEGG pathway analyses indicated the co-expressed genes of CD146 were mainly related to a variety of immune-related pathways, including Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation, Th17 cell differentiation, and leukocyte transendothelial migration. Our data demonstrated that the expression and methylation status of CD146 were strongly correlated with immune infiltration levels, immunomodulators, and chemokines. Further, the sensitivity and resistance of renal cancer cell lines to some drugs were related to CD146 expression.
Conclusions: Our study highlights the clinical significance of CD146 in ccRCC and provides novel insights into the immune function of CD146 in the tumor microenvironment.
Keywords: CD146; ccRCC; methylation; prognosis; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2021 Lv, Feng, Tao, Li and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
High GTSE1 expression promotes cell proliferation, metastasis and cisplatin resistance in ccRCC and is associated with immune infiltrates and poor prognosis.Front Genet. 2023 Mar 14;14:996362. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.996362. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 36999057 Free PMC article.
-
PLK4 Is a Potential Biomarker for Abnormal Tumor Proliferation, Immune Infiltration, and Prognosis in ccRCC.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Sep 20;2022:6302234. doi: 10.1155/2022/6302234. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. PMID: 36176741 Free PMC article.
-
POLD1 as a Prognostic Biomarker Correlated with Cell Proliferation and Immune Infiltration in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 6;24(7):6849. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076849. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047824 Free PMC article.
-
RAB42 is a Potential Biomarker that Correlates With Immune Infiltration in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 May 26;9:898567. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.898567. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35720121 Free PMC article.
-
PTPRO predicts patient prognosis and correlates with immune infiltrates in human clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Transl Cancer Res. 2020 Aug;9(8):4800-4810. doi: 10.21037/tcr-19-2808. Transl Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 35117843 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Identification of IL20RB as a Novel Prognostic and Therapeutic Biomarker in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.Dis Markers. 2022 Mar 8;2022:9443407. doi: 10.1155/2022/9443407. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 35299868 Free PMC article.
-
AQP5 Is a Novel Prognostic Biomarker in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 May 10;12:890193. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.890193. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35619903 Free PMC article.
-
High GTSE1 expression promotes cell proliferation, metastasis and cisplatin resistance in ccRCC and is associated with immune infiltrates and poor prognosis.Front Genet. 2023 Mar 14;14:996362. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.996362. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 36999057 Free PMC article.
-
Melanoma Cell Adhesion Molecule Plays a Pivotal Role in Proliferation, Migration, Tumor Immune Microenvironment, and Immunotherapy in Colorectal Cancer.Cancer Med. 2025 Mar;14(5):e70740. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70740. Cancer Med. 2025. PMID: 40042109 Free PMC article.
-
Melanoma Cell Adhesion Molecule (CD 146) in Endometrial Physiology and Disorder.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025;1474:131-148. doi: 10.1007/5584_2024_826. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 39400880 Review.
References
-
- Choueiri TK, Halabi S, Sanford BL, Hahn O, Michaelson MD, Walsh MK, et al. . Cabozantinib Versus Sunitinib As Initial Targeted Therapy for Patients With Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma of Poor or Intermediate Risk: The Alliance A031203 CABOSUN Trial. J Clin Oncol (2017) 35:591–7. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.70.7398 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Motzer RJ, Barrios CH, Kim TM, Falcon S, Cosgriff T, Harker WG, et al. . Phase II Randomized Trial Comparing Sequential First-Line Everolimus and Second-Line Sunitinib Versus First-Line Sunitinib and Second-Line Everolimus in Patients With Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. J Clin Oncol (2014) 32:2765–72. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.54.6911 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

