The Application of Wearable Glucose Sensors in Point-of-Care Testing
- PMID: 34957071
- PMCID: PMC8692794
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.774210
The Application of Wearable Glucose Sensors in Point-of-Care Testing
Abstract
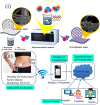
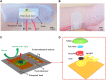
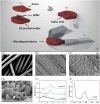
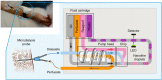
Diabetes and its complications have become a worldwide concern that influences human health negatively and even leads to death. The real-time and convenient glucose detection in biofluids is urgently needed. Traditional glucose testing is detecting glucose in blood and is invasive, which cannot be continuous and results in discomfort for the users. Consequently, wearable glucose sensors toward continuous point-of-care glucose testing in biofluids have attracted great attention, and the trend of glucose testing is from invasive to non-invasive. In this review, the wearable point-of-care glucose sensors for the detection of different biofluids including blood, sweat, saliva, tears, and interstitial fluid are discussed, and the future trend of development is prospected.
Keywords: biofluids; glucose sensor; non-invasive; point-of-care testing; wearable.
Copyright © 2021 Zhang, Zeng, Wang, Feng, Song, Zhao, Wang and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Fluid-based wearable sensors: a turning point in personalized healthcare.Turk J Chem. 2023 May 22;47(5):944-967. doi: 10.55730/1300-0527.3588. eCollection 2023. Turk J Chem. 2023. PMID: 38173754 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review on the Advanced Techniques of Wearable Point-of-Care Devices and Their Futuristic Applications.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Feb 28;13(5):916. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13050916. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36900059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Achievements and Challenges for Real-Time Sensing of Analytes in Sweat within Wearable Platforms.Acc Chem Res. 2019 Feb 19;52(2):297-306. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.8b00555. Epub 2019 Jan 28. Acc Chem Res. 2019. PMID: 30688433 Review.
-
Wearable physiological systems and technologies for metabolic monitoring.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2018 Mar 1;124(3):548-556. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00407.2017. Epub 2017 Sep 28. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2018. PMID: 28970200 Review.
-
Enzyme-Based Glucose Sensor: From Invasive to Wearable Device.Adv Healthc Mater. 2018 Apr;7(8):e1701150. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201701150. Epub 2018 Jan 15. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018. PMID: 29334198 Review.
Cited by
-
Three-Phases Interface Induced Local Alkalinity Generation Enables Electrocatalytic Glucose Oxidation in Neutral Electrolyte.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Apr 28;10:909187. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.909187. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35573243 Free PMC article.
-
Biosensors toward behavior detection in diagnosis of alzheimer's disease.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Oct 19;10:1031833. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.1031833. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36338126 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Advances in Antenna Design toward Wearable Devices Based on Nanomaterials.Biosensors (Basel). 2024 Jan 10;14(1):35. doi: 10.3390/bios14010035. Biosensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38248412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review on Carbon-Based Micro and Nano Electro-Mechanical Systems for Biotechnological Application.Recent Pat Nanotechnol. 2025;19(4):468-482. doi: 10.2174/0118722105293232240826135124. Recent Pat Nanotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40356384 Review.
-
Wearable Multi-Functional Sensing Technology for Healthcare Smart Detection.Micromachines (Basel). 2022 Feb 2;13(2):254. doi: 10.3390/mi13020254. Micromachines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35208378 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

